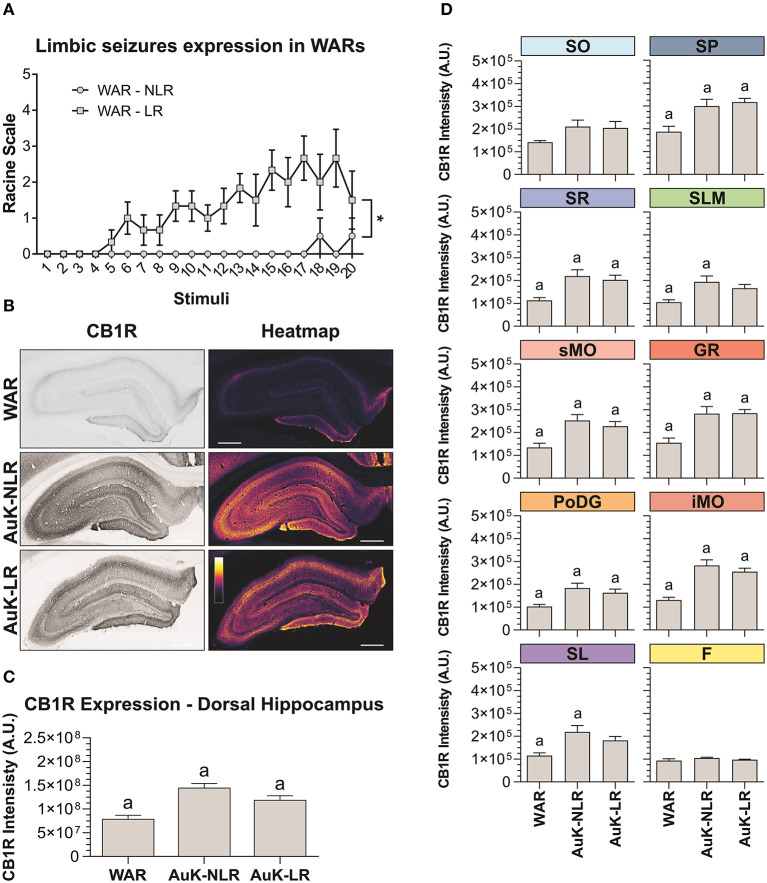
Figure 4.
CB1R immunostaining in the hippocampus after chronic seizures: WARs with limbic recruitment (LR) and WARs with no limbic recruitment (NLR). (A) Limbic seizure expression in WARs during the audiogenic kindling (AuK). Squares represent limbic seizure progression in WARs with limbic recruitment (LR). Circles represent limbic seizure progression in WARs with no limbic recruitment (NLR). Seizures were analyzed according to the Racine's scale (Racine, 1972). (B) Representative images of CB1R immunostaining in the dorsal hippocampus in different experimental groups (left column) and their correspondent heatmap (right column). (C) CB1 immunostaining in the total hippocampal area of WARs (n = 5) compared to WARs after the AuK with limbic recruitment (LR, n = 6) and with no limbic recruitment (NLR, n = 4). (D) CB1R signal intensity in different hippocampal layers. Stratum oriens (SO), stratum pyramidale (SP), stratum radiatum (SR), stratum lacunosum moleculare (SLM), superior molecular layer (sMO), inferior molecular layer (iMO), dentate gyrus granular cell layer (GR), polymorph layer of the dentate gyrus (PoDG), stratum lucidum (SL), fimbria (F). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error mean (SEM). Equal letters represent significant differences (p < 0.05) between groups: “a” in comparison to WAR. Scale bar: 500 μm. Color code scale (8 bits image): 0–255 (min–max).