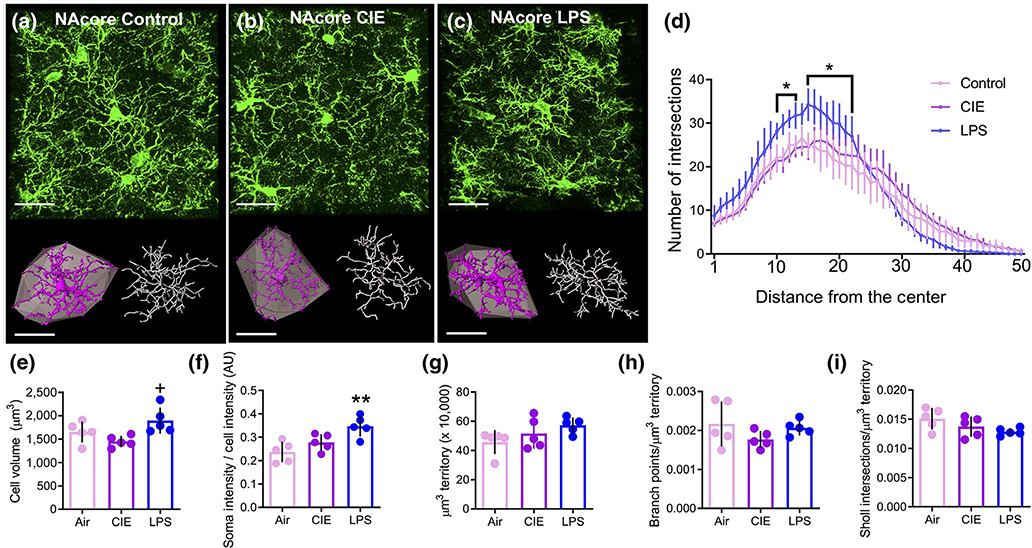
FIGURE 7.
Differential effects of chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on microglial complexity were not observed in the NAcore. (a-c) Raw data (green), digitized single-cells (purple) and associated convex hulls (grey), as well as skeletonizations (white) for NAcore microglia in (a) control, (b) CIE-exposed, and (c) LPS-exposed rats. (d) Sholl analysis revealed that LPS exposure resulted in a greater number of breaks (in 1 μm intervals) closer to the center of the cell compared to control rats. (e) LPS increased the microglia cell volume compared to control, but CIE was without an effect. (f) LPS, but not CIE, increased the normalized Iba1 intensity in the somatic compartment. (g) There was no difference between groups in the territory occupied by individual microglia. (h) When normalized to the territory occupied, there was no difference between groups in the number of branch points. (i) The number of Sholl intersections normalized to the hull volume was not different between groups in the NAcore. **p < 0.01 compared to control, +p < 0.05 compared to CIE. Scale bars = 20 μm