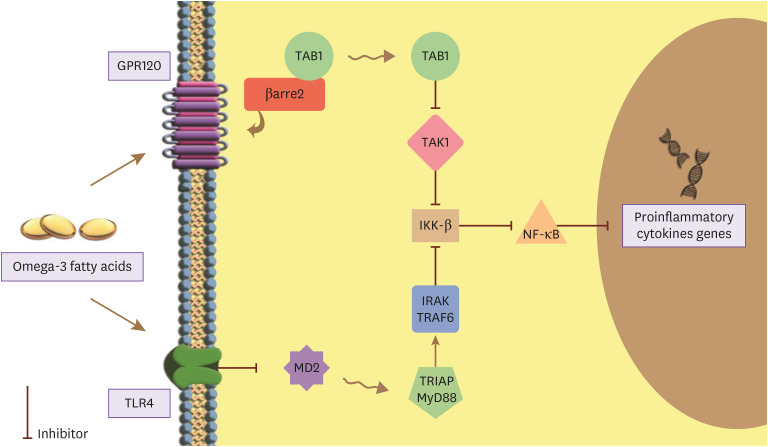
Figure 2. How omega-3 fatty acids impact the cellular immune response.
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine triggering an inflammatory response via activation of transcription of genes for further pro-inflammatory proteins. Omega-3 fatty acids potentially exert their anti-inflammatory effect via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway and G-protein coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) pathway to inhibit the NF-κB and consequently the inflammatory cascade.
TAB, TGF-beta activated kinase; TAK, tat-associated kinase; IRAK, interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6; TRIAP, TP53 regulated inhibitor of apoptosis; MD2, myeloid differentiation factor 2.