Figure 3.
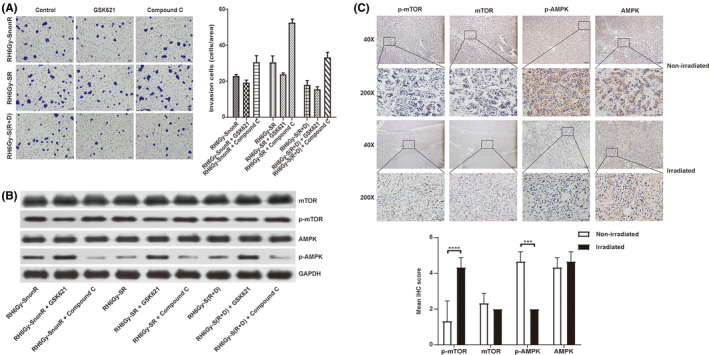
Irradiated supernatant (SR) promotes hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell migration and invasion by inhibiting the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. A, The effects of nonirradiated (SnonR), irradiated (SR), and irradiated plus drug (celecoxib)‐treated S(R + D) supernatant on RH6Gy cell invasion were examined by transwell invasion assays. SR enhanced the invasiveness of RH6Gy cells, GSK621 reduced invasion ability, and compound C enhanced invasion ability in all three groups of RH6Gy cells (RH6Gy‐SnonR, RH6Gy‐SR, and RH6Gy‐S[R + D]). B, Representative Western blot showing the levels of p‐AMPK, AMPK, p‐mTOR, and mTOR in RH6Gy‐SnonR, RH6Gy‐SR, and RH6Gy‐S(R + D) cells; GAPDH served as an internal control. C, Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of p‐mTOR, mTOR, p‐AMPK, and AMPK and representative images of 14 samples, including HCC patients who received neoadjuvant radiotherapy (N = 7) or did not receive radiotherapy (N = 7). Magnification: 40× (first and third panels), 200× (second and fourth panels). IHC score of p‐mTOR, mTOR, p‐AMPK, and AMPK in HCC tissue. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001
