-
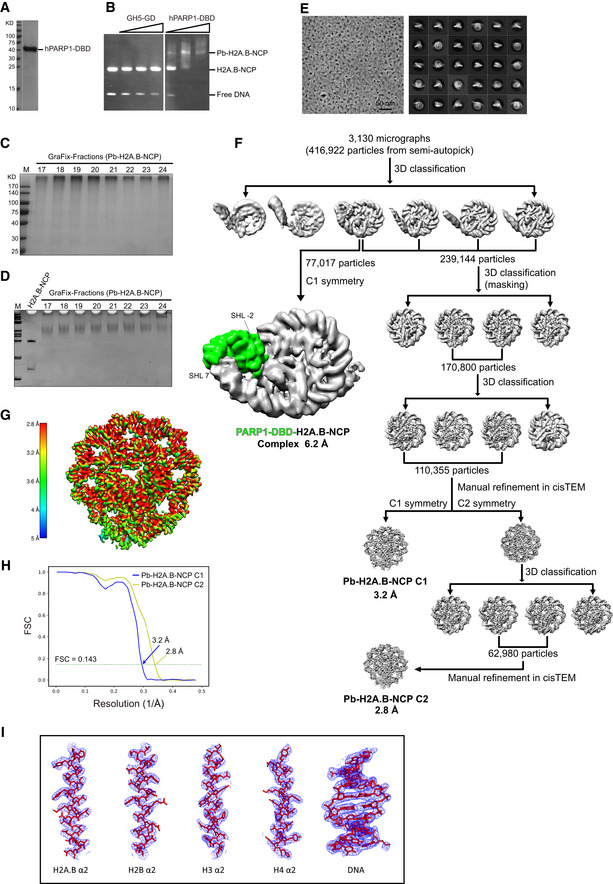
A
SDS–PAGE analysis of the purified human PARP1 DNA binding domain (hPARP1‐DBD).
-
B
EMSA analyses of H2A.B‐NCP interacting with linker histone H5 and PARP1 DNA binding domain. Chicken H5 residues 22–102 (GH5‐GD) and human PARP1 DNA binding domain (hPARP1‐DBD) were added in two‐ or fourfold molar excess.
-
C, D
SDS–PAGE (C) and Native‐PAGE (D) analyses of Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP subject to GraFix treatment. H2A.B‐NCP bound to PARP1 DNA binding domain (Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP) were subjected to 10–30% glycerol gradient centrifugation with 0–0.15% glutaraldehyde. Peak fractions (19–20) containing intact Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP were processed for further electron microscopy analysis. Experiments were repeated multiple times (n > 10).
-
D
Representative cryo‐EM image (left) and 2D class averages (right) of Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP particles.
-
E
Flow chart of data processing of the Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP particles. Highlighted with green color refers to the extra density corresponding to hPARP1‐DBD.
-
F
The final 3D density map of Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP shown in the indicated views is colored according to the local resolution estimated by the software ResMap.
-
G
FSC curves of the final density maps of the Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP C1 (blue) and the Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP C2 (yellow). Reported resolutions were based on the FSC = 0.143 criteria.
-
H
Examples of cryo‐EM density maps of the histones and DNA in Pb‐H2A.B‐NCP generated in Pymol.