Figure 7. Model of condensin role in the minimization of DNA entanglements.
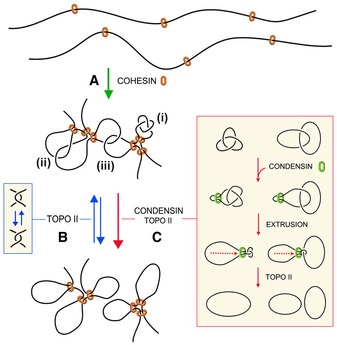
- Cohesin generates and stabilizes DNA loops to organize interphase chromatin into topological domains.
- Random DNA strand passage activity of topo II can either remove or produce DNA entanglements within and across such topological domains. Juxtapositions of DNA segments within a loop can lead to the formation of knots (i), whereas juxtapositions of DNA segments belonging to nearby loops or adjacent domains can lead to the formation of intra‐ (ii) or inter‐molecular (iii) DNA interlinks.
- To minimize the occurrence of these entanglements, condensin might use its DNA loop extrusion activity to constrict intra‐ and inter‐molecular interlinks and so bias the DNA strand passage activity of topo II to remove them. This condensin function may operate during interphase to facilitate chromatin transactions and during cell division to enforce the removal of sister chromatid interlinks.
