Figure 6. TP53 is activated through a distinct pathway in a microcephaly model caused by the loss of Smc5 .
-
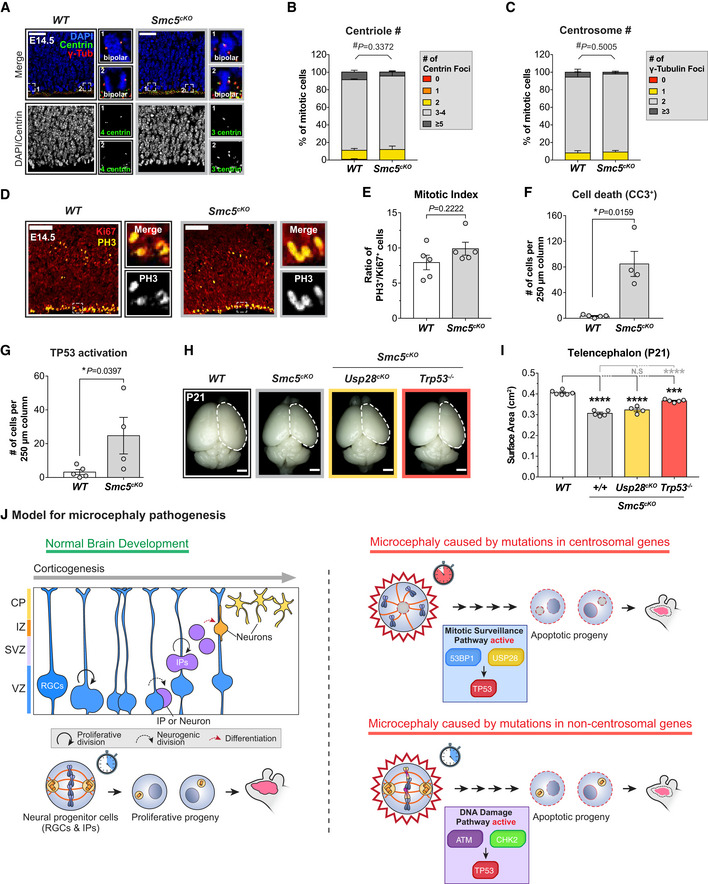
AWT and Smc5cKO cortices at E14.5 stained with antibodies against centrin (green), γ‐tubulin (red) and DAPI (blue). Insets showing zoomed in view of 2 representative cells. Scale bar = 25 μm.
-
B, CQuantification of the number of (B) centrin foci and (C) γ‐tubulin foci in mitotic cells in the VZ of E14.5 cortices. WT n = 175 cells, N = 4 embryos; Smc5cKO n = 134 cells, N = 3 embryos. #, chi‐square test. WT data are from Fig EV1F and G and shown alongside for comparison.
-
DE14.5 cortices stained with antibodies against Ki67 (red) and phosphorylated‐Histone H3 (PH3, yellow). Insets showing zoomed in view of cells in the VZ and SVZ. Scale bar = 100 μm.
-
ERatio of mitotic (PH3+) to cycling (Ki67+) cells in E14.5 cortices. WT N = 5, Smc5cKO N = 5; two‐tailed Mann–Whitney t‐test. WT data are from Fig 1H and shown alongside for comparison.
-
F, GQuantification of the number of (F) apoptotic cells (CC3+) and (G) cells with TP53 activation within a 250 μm‐width column of E14.5 cortices. WT N = 5, Smc5cKO N = 4; two‐tailed Mann–Whitney t‐test. WT data are from Fig 4E and F and shown alongside for comparison.
-
HRepresentative whole mount images of WT, Smc5cKO, Smc5cKO;Usp28cKO, Smc5cKO;Trp53 −/− brains at P21. Scale bar = 0.2 cm.
-
ITelencephalon area of P21 brains of the indicated genotypes. WT littermates N = 6, Smc5cKO N = 5, Smc5cKO;Usp28cKO N = 4, Smc5cKO;Trp53 −/− N = 5; one‐way ANOVA with post hoc analysis.
-
JModel for two TP53‐dependent pathways underlying primary microcephaly. In the first model, NPCs with mutations in centrosome genes take longer to assemble their spindle in mitosis. This delay triggers the activation of the mitotic surveillance pathway, which activates TP53 through 53BP1 and USP28. By contrast, in microcephaly caused by mutations in genes required for DNA repair or genome stability, centrosome function and mitotic duration are unaffected. Instead, accumulated DNA lesions trigger DNA damage signaling in NPCs to activate TP53. In both models, increased TP53 activity leads to apoptosis, thus depleting the NPC pool and decreasing the final number of neurons.
Data information: All data represent the means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ***< 0.001; ****< 0.0001 and not significant indicates P > 0.05. See also Fig EV6.
