Figure 1. CELF6 Primarily Associates with 3′ UTRs of Target mRNAs In Vivo.
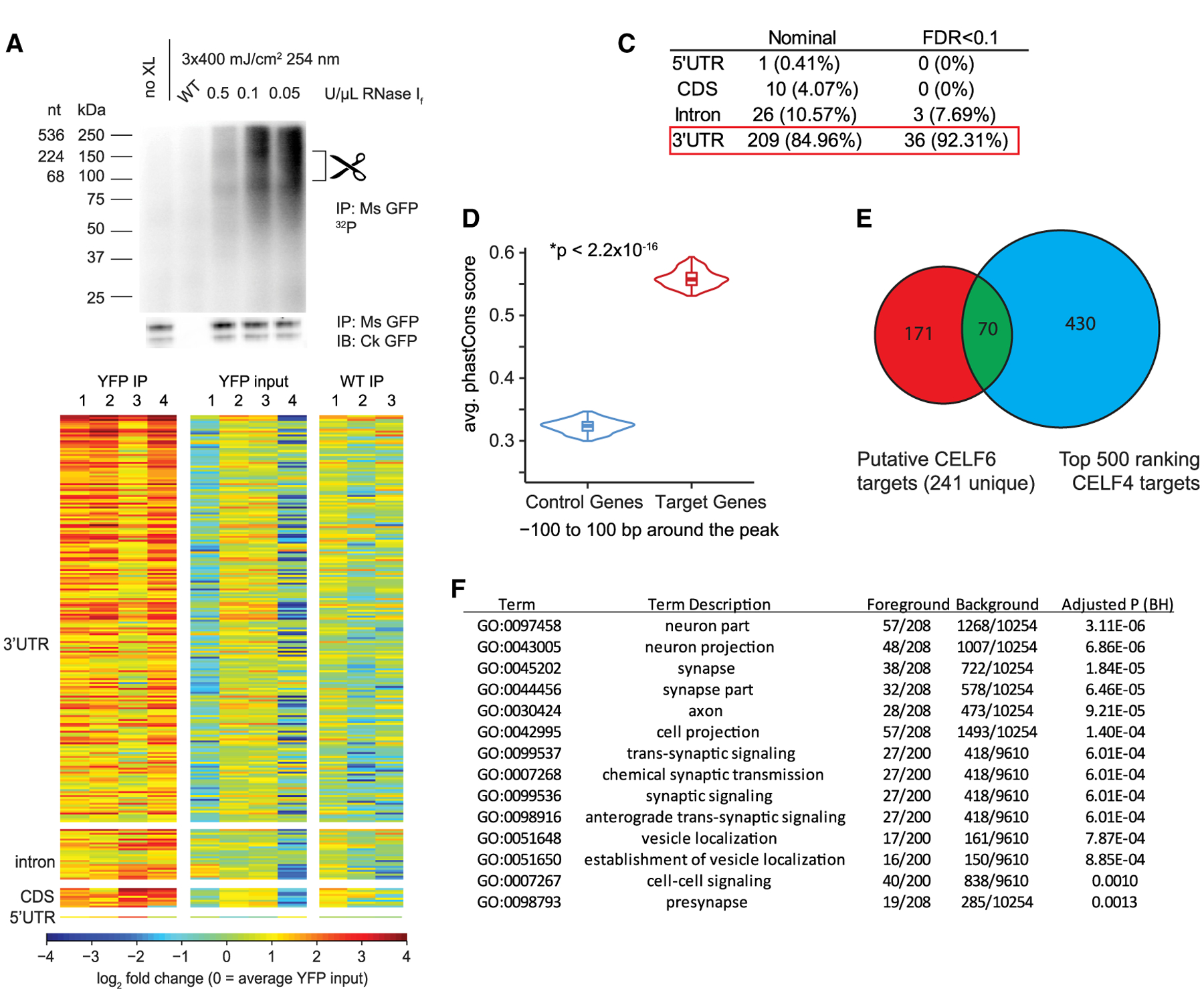
(A) CELF6 CLIP, lanes: no crosslink (no XL), wild-type (WT) control, and three concentrations of RNase If. Top: RNA 32P autoradiogram. Bottom: anti-GFP immunoblot. Scissors mark region (80–150 kDa) above CELF6-HA/YFP (78 kDa) isolated for sequencing. Immunoblot detects two bands, corresponding to sizes of known isoforms of CELF6.
(B) Log2 counts-per-million (CPM) RNA in four CELF6-HA/YFP+ replicates and three WT replicates differentially abundant regions. Heatmaps show enrichment in HA/YFP+ immunoprecipitate (IP) samples relative to input and WT controls. CPM is normalized to mean YFP input by row.
(C) Summary of differential enrichment analysis of genes showing nominally significant (p < 0.05), and Benjamini-Hochberg (FDR < 0.1) enrichment in HA/YFP+ IP samples relative to both HA/YFP+ input and WT IP controls. No peaks were found in intergenic regions.
(D) Average phastCons score for ±100 bp around CLIP peaks in targets compared with control genes not exhibiting enrichment in CLIP (p < 2.2 × 10−16, two-tailed t test).
(E) Overlap of CELF6 and CELF4 targets identified in Wagnon et al. (2012).
(F) DAVID gene ontology analysis of CELF6 CLIP targets (241 unique genes).
