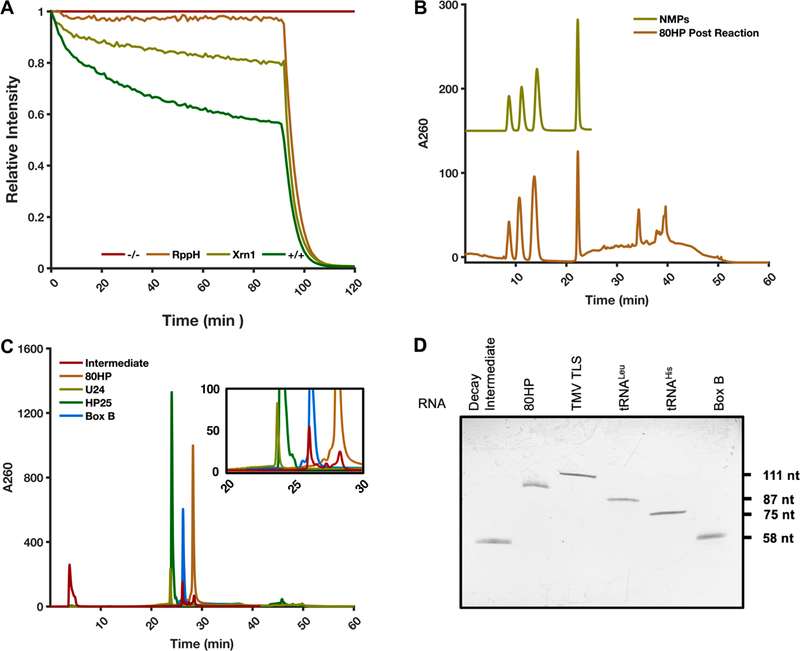
Figure 3.
Interrogation of ScXrn1ΔC products. (A) Typical TRFRD assay using ScXrn1ΔC with the addition of RNase A at 90 min. The “−/−” trace shown in red is a no enzyme control. The “+/+” trace shown in green contains both RppH and ScXrn1ΔC. Conditions: 2 μM 80HP RNA, 2 μM BdRppH, 0.05 μM ScXrn1ΔC, and 5 units of RNase A in 1xEC3K+ buffer at pH 7.9 and 37 °C. (B) HPLC trace of products from bulk reaction of 80HP RNA with ScXrn1ΔC (bottom trace). The top trace is the four purified 5′NMPs resolved using TBAP-modified C-18 chromatography. (C) HPLC analysis of the 80HP RNA with and without ScXrn1ΔC in the presence of DFHBI using PLRP-S chromatography overlaid with the trace of three oligonucleotide-length markers: U24 (24 nucleotides), HP25 (25 nucleotides), and Box B (58 nucleotides). The inset is a region of the trace where the DFHBI-dependent resistant RNA population appears during the reaction. We have not yet fully characterized the intermediate products, but their size roughly corresponds to the size of the iSpinach aptamer, indicating degradation up to the quadruplex DFHBI binding pocket. (D) dPAGE of the intermediate compared against the full-length 80HP construct and various RNA constructs as size markers. The intermediate appears to be approximately the same size as the 58-nucleotide Box B RNA.