FIG. 4.
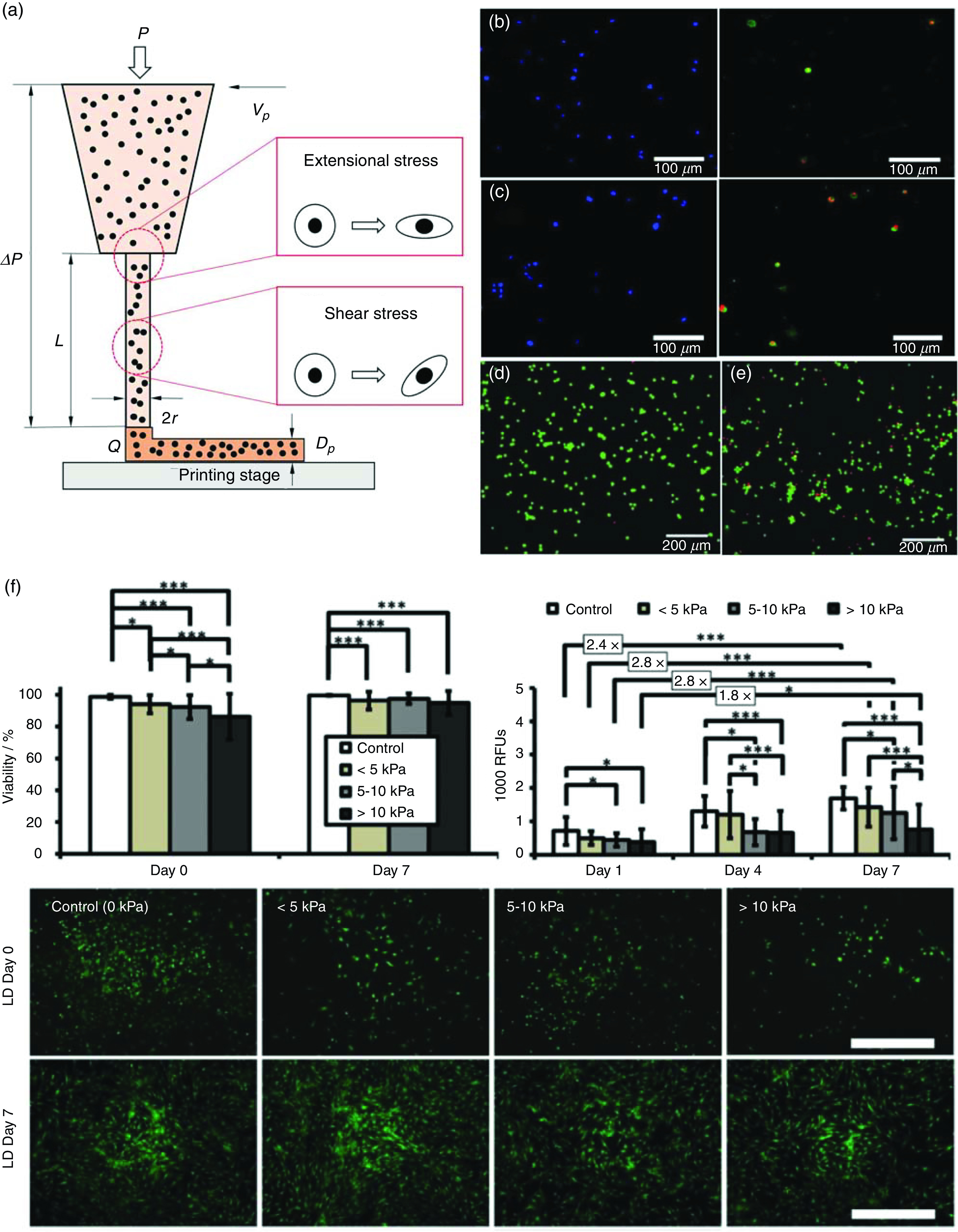
Examining cell deformation and damages under mechanical forces during 3D bioprinting. (a) Schematic illustration of the 3D bioprinting process and the mechanical stresses involved. (b) and (c) Schwann cell membrane rupture and damage in bioprinting with applied bioprinting pressures of 100 kPa (b) and 400 kPa (c). (d) and (e) Live/dead assay of fibroblasts under no shearing (d) and shearing [(e), 1700 Pa]. (f) Short-term and long-term impact of different bioprinting-induced shear stress levels on human mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) viability and proliferation. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (b) and (c) Reproduced with permission from Ning et al., ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 4, 3906 (2018). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.47 (d) and (e) Reproduced with permission from Ning et al., Tissue Eng., Part C 22, 652 (2016). Copyright 2016 Mary Ann Liebert.79 (f) Reproduced with permission from Blaeser et al., Adv. Healthcare Mater. 5, 326 (2016). Copyright 2016 John Wiley and Sons.46
