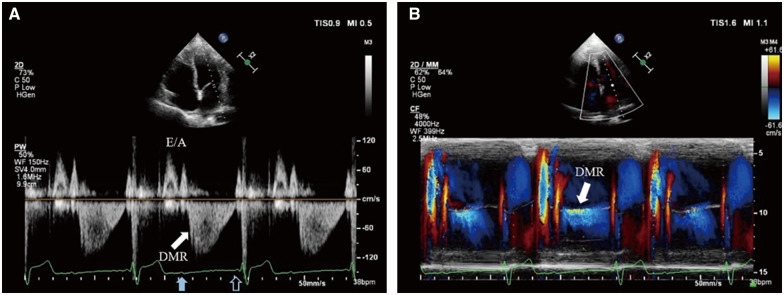
Figure 1.
P-waves with 2:1 relation with QRS complexes are displayed on the electrocardiogram. Transthoracic echocardiography: (A) PW Doppler of transmitral flow from the apical four-chamber view. After left ventricular systole, the spectrum demonstrates normal early diastolic filling E wave and left atrium contractive A wave. After the blocked sinus P-wave (solid blue arrow), diastolic mitral regurgitation (solid white arrow) appears immediately until next left atrium contraction matching the conducted sinus P-wave (hollow blue arrow). The flow velocity of diastolic mitral regurgitation is about 1.1 m/s (far lower than common systolic mitral regurgitation and slightly higher than A wave) and gradually diminishes. (B) Colour M-mode of transmitral flow from the apical four-chamber view. Diastolic mitral regurgitation presents between the two mitral valve forward flows driven by left atrium contraction (solid white arrow).