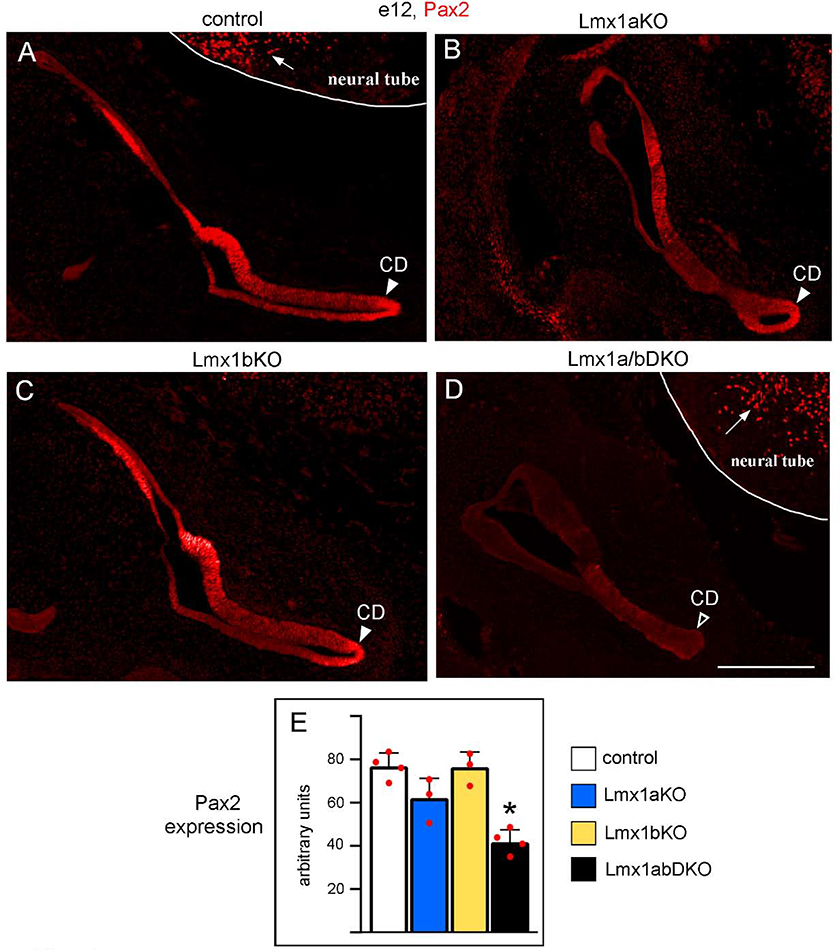
Fig. 4. Simultaneous but not individual loss of Lmx1a and Lmx1b reduces Pax2 expression in the inner ear.
Transverse sections of the e12 inner ear immunostained with an anti-Pax2 antibody. Pax2 was strongly expressed in the inner ear, including the developing cochlear duct (CD, arrowhead) in control (A), Lmx1a KO (B) and Lmx1b KO (C) embryos. Pax2 expression appeared reduced in the inner ear, including the developing CD, of Lmx1a/b DKO embryos (D, open arrowhead). Note that Pax2 was similarly expressed in the neural tube of Lmx1a/b DKO and control embryos (arrows in A and D) indicating that double loss of Lmx1a and Lmx1b reduced Pax2 expression specifically in the ear. (E) Quantification of Pax2 immunostaining intensity revealed no statistically significant difference between control, Lmx1a KO and Lmx1b KO inner ears (p>0.05), but a reduction of Pax2 expression in the inner ear of Lmx1a/b DKO embryos (asterisk) relative to control (p<0.001), Lmx1a KO (p=0.014) and Lmx1b KO (p<0.001) embryos. n=4 control, n=3 Lmx1a KO, n=3 Lmx1b KO, and n=4 Lmx1a/b DKO embryos. Scale bar: 200 μm.