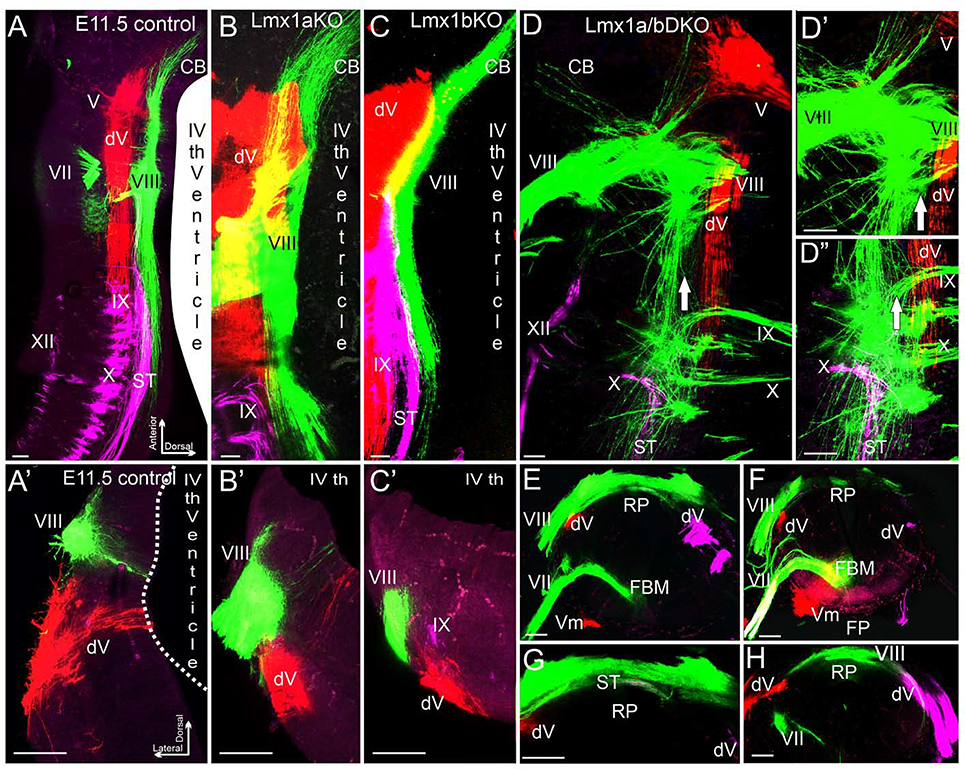
Fig. 5. Inner ear central vestibular projections aberrantly target the hindbrain roof plate in e11.5 Lmx1a/b DKO embryos.
Whole mounted hindbrains (A-D”) and transverse hindbrain sections (A’-C’, E-H) from e11.5 embryos of indicated genotypes. Discrete sensory afferent projections were visualized by labeling distinct cranial nerves (indicated by Roman numbers) with lipophilic dyes. V - trigeminal nerve, dV - descending trigeminal tract, VII - facial nerve, VIII – inner ear vestibular nerve, IX - glossopharyngeal nerve, X - vagus nerve, XII - hypoglossal nerve. (A-C, A’-C’) In control, Lmx1a KO, and Lmx1b KO embryos, different afferent projections run parallel to the anterior-posterior axis of the hindbrain, do not significantly overlap with each other, and do not cross the dorsal midline occupied by the wide choroid plexus epithelium derived from the IVth ventricle roof plate.
(D-D”) Dorsal whole mount view showing that in Lmx1a/b DKO embryos, inner ear vestibular (VIII), trigeminal (V), and solitary tract (ST) afferents extend aberrantly close to or cross the dorsal midline. Arrow (D-D”) shows location of the dorsal midline, which is heavily populated by inner ear vestibular (VIII) afferent fibers. D’ and D” are high power views of D.
(A’-C’, E-H) Transverse hindbrain sections showing that similar to control, Lmx1a KO and Lmx1b KO embryos, in Lmx1a/b DKO hindbrain, the descending trigeminal tract (dV) was located ventral to inner ear vestibular (VIII) fibers. However, in contrast to control, Lmx1a KO and Lmx1b KO embryos (A’-C’), inner ear vestibular (VIII) fibers extended to and populated the dorsal midline roof plate (RP) covering the central canal in Lmx1a/b DKO littermates (E-H). Note the near normal location of facial branchial motor neurons (FBM) and ventral motor neurons (Vm) in the Lmx1a/b DKO (E, F) near the floor plate (FP), and solitary tract afferents crossing the roof plate (G). G is a high power view of E, without the magenta channel; panels F and H show two different sections from another embryo.
Scale bar: 100 μm.