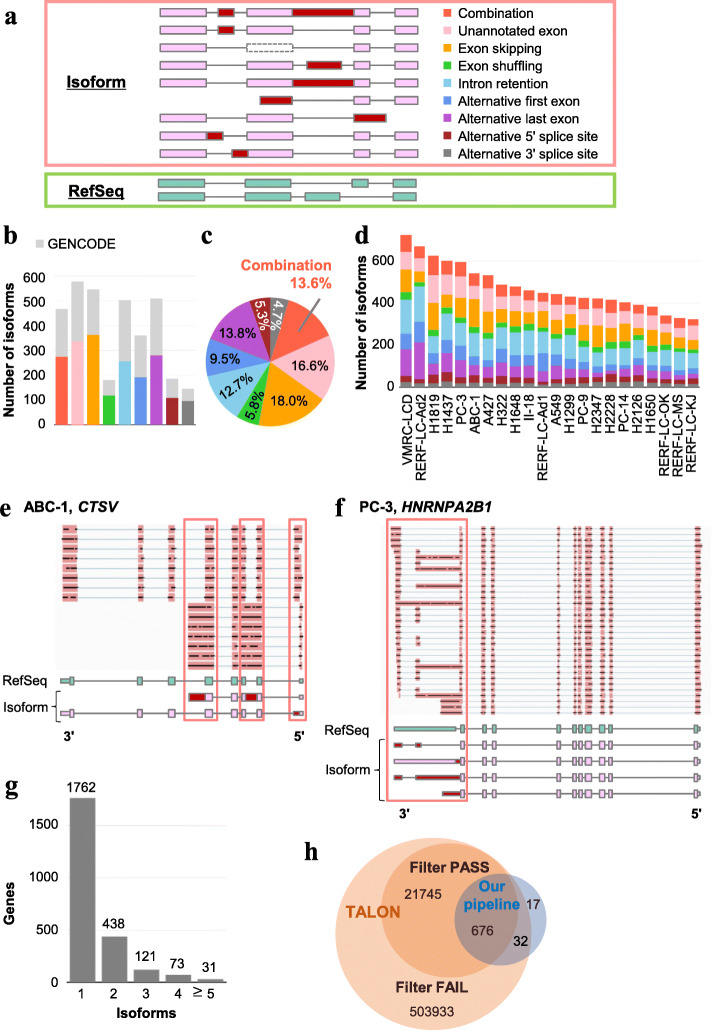
Fig. 1.
Identification of aberrant splicing isoforms in cell lines. a Classification of aberrant splicing events. Pink boxes represent constitutively spliced exons. Red and dotted-line boxes represent alternatively spliced exons. b The number of isoforms classified for each splicing event shown in a. Light gray bars indicate isoforms represented in GENCODE and other-colored bars indicate unannotated isoforms. c The proportion of splicing events in unannotated isoforms. The color key is shown in a. d The number of splicing isoforms and the proportion of each splicing event in cell lines. The color key is shown in a. e The full-length structure of the splicing isoform of CTSV in ABC-1. Some MinION reads show a combination pattern of intron retention, alternative last exon, and alternative 5′ splice site. f The full-length structure of splicing isoforms of HNRNPA2B1 in PC-3. Some MinION reads indicate extensive alternative splicing within its 3′ UTR. g The number of isoform patterns per gene in the cell lines. h A comparison of the number of isoforms in VMRC-LCD derived from our pipeline and from the TALON pipeline (99% of the isoforms we detected were included in the TALON results)