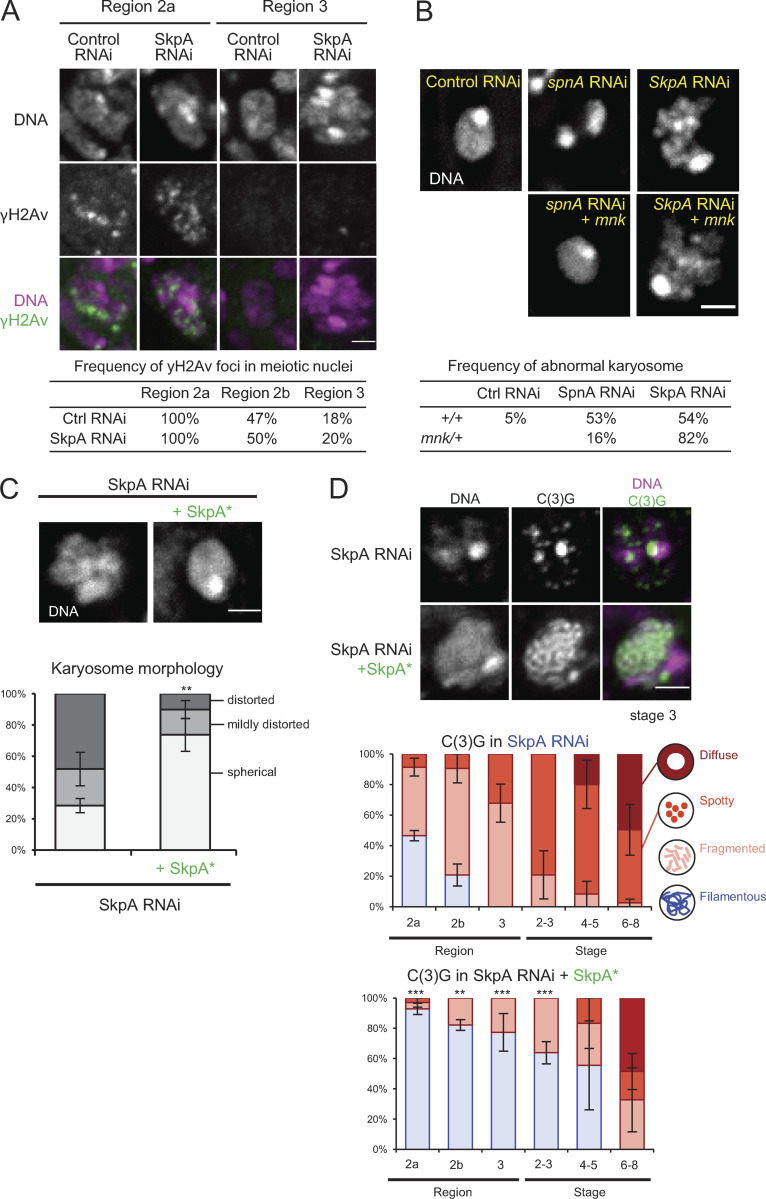
Figure S1.
SkpA depletion does not affect the timing of DSB formation and repair, and the karyosome defect is independent of the meiotic recombination checkpoint. (A) Immunostaining of γH2Av, which marks DNA double-strand breaks alongside DNA staining, and frequencies of γH2Av foci in meiotic nuclei in control and SkpA RNAi. Meiotic cells were identified by costaining of C(3)G. A total of 14–17 germaria were counted for each region. (B) DNA staining of the karyosomes in spnA and SkpA RNAi oocytes with or without a heterozygous mnk (Chk2) mutation, and frequencies of abnormal karyosome morphology. The karyosome abnormality is independent of the meiotic recombination checkpoint. Enhancement of karyosome defects by a mnk mutation is common and not specific to SkpA or SCF. A total of 19–39 oocytes were counted for each genotype. Control RNAi, nos-GAL4(MVD1)/UASp-shRNA(white); spnA RNAi, nos-GAL4(MVD1)/UASp-shRNA(spnA); SkpA RNAi, nos-GAL4(MVD1)/UASp-shRNA(SkpA); spnA RNAi +mnk, nos-GAL4(MVD1) mnkp6/UASp-shRNA(spnA); SkpA RNAi +mnk, nos-GAL4(MVD1) mnkp6/UASp-shRNA(SkpA). (C) DNA staining of karyosomes in SkpA RNAi oocytes with or without a wild-type RNAi-resistant SkpA transgene (SkpA*) expressed under the ubiquitin promoter, and frequencies of karyosome morphologies. Scale bar = 2 µm. Error bars represent SEM from triplicated experiments representing 49–52 oocytes for each genotype. SkpA RNAi, nos-GAL4(MVD1)/UASp-shRNA(SkpA); SkpA RNAi +SkpA*, nos-GAL4(MVD1) Ub-SkpA(RNAi resistant)/UASp-shRNA(SkpA). (D) Localization patterns of the synaptonemal complex component C(3)G in SkpA RNAi with or without a wild-type RNAi-resistant SkpA transgene. Scale bars = 2 µm. Error bars represent SEM from triplicated experiments representing a total of 11–23 germaria/oocytes for each region/stage. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.