FIGURE 2.
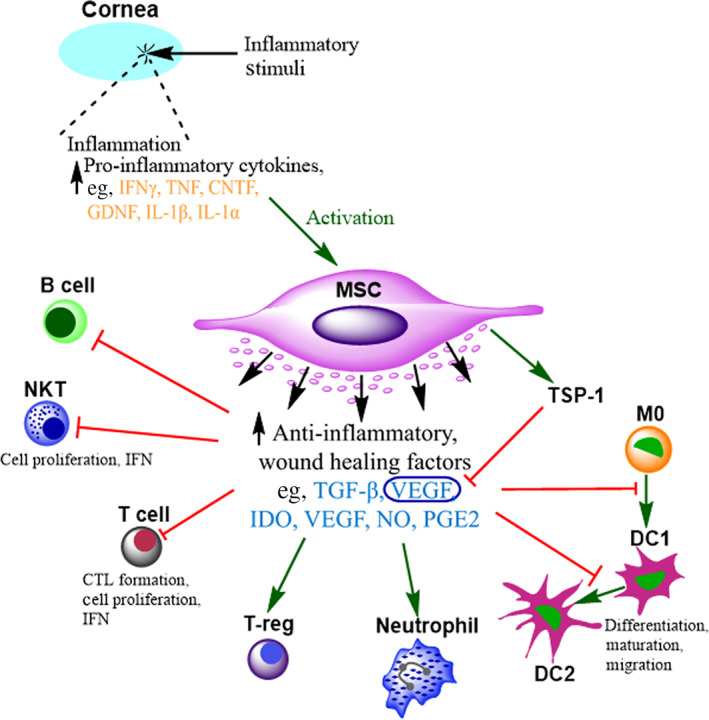
Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Inflammatory stimuli at the ocular surface results in an increase in pro‐inflammatory factors, for example interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), glial cell‐line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and interleukins (IL) 1β and 1α. These factors can activate and stimulate any applied MSCs to secrete immunomodulatory factors including transforming growth factor β (TGF‐β), IL‐10, indoleamine 2,3‐dioxygenase (IDO), nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). This can result in the inhibition (red line) of proliferation and function of T and B lymphocytes, natural killer T cells (NKTs), and dendritic cells (DCs), however, can preserve neutrophil viability through apoptosis inhibition. MSCs also stimulate (green arrow) the upregulation of thrombospondin‐1 (TSP‐1) in the cornea, which inhibits VEGF and prevents angiogenesis
