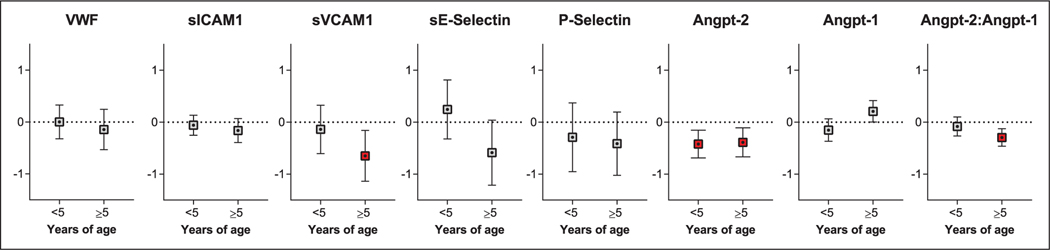
Figure 3.
Estimates from linear mixed-effects modeling evaluating endothelial activation and longitudinal age-adjusted z scores in cognition by age group. Estimates (95% CI) from linear mixed-effects models evaluating longitudinal changes in age-adjusted z scores in children with severe malaria based on the log10 concentrations in endothelial markers at admission. All models adjusted for disease severity at presentation (presence of coma, number of seizures during hospitalization, acute kidney injury) and sociodemographic factors (age, sex, weight-for-age and height-for-age z scores, socioeconomic status, home environment, parental education, and preschool attendance). The false discovery rate was applied at a threshold of 0.05 adjusting for eight comparisons in each age group. Relationships significant following adjustment for multiple testing are indicated in red. Angpt-1 = angiopoietin-1, Angpt-2 = angiopoietin-2, sE-Selectin = soluble E-Selectin, sICAM-1 = soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1, sVCAM-1 = soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, vWF = von Willebrand factor.