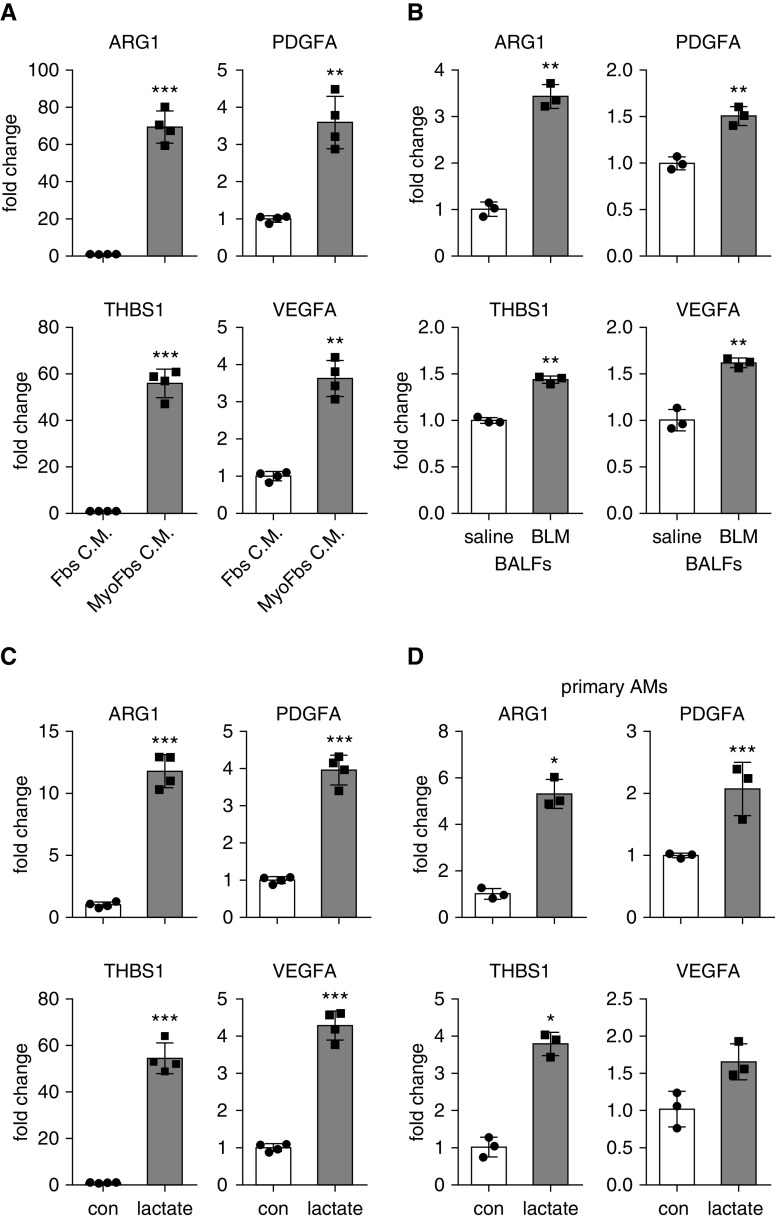
Figure 3.
Lung myofibroblast–conditioned media, BALFs from mice with lung fibrosis, or lactate promote macrophage profibrotic phenotype. (A) Bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs) were treated with conditioned media from normal fibroblasts or TGF-β1–induced myofibroblasts. Twenty-four hours after treatment, cells were harvested, and concentrations of the indicated genes were determined by real-time PCR (n = 4; mean ± SD). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test. (B) BMDMs were treated with BALFs from mice that were treated i.t. with saline or BLM for 3 weeks. Twenty-four hours after treatment, concentrations of the indicated genes were determined by real-time PCR. n = 3; mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 by two-tailed Student’s t test. (C) BMDMs were treated with or without 20 mM lactate for 24 hours. Cells were harvested, and concentrations of the indicated genes were determined by real-time PCR (n = 4; mean ± SD). ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test. (D) Primary alveolar macrophages) were isolated from BALFs of C57BL/6 mice and treated with 20 mM lactate for 24 hours. Concentrations of the indicated genes were determined by real-time PCR (n = 3; mean ± SD). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test. AM = alveolar macrophage; con = control; Fbs C.M. = fibroblast-conditioned media; MyoFbs C.M. = myofibroblast-conditioned media.