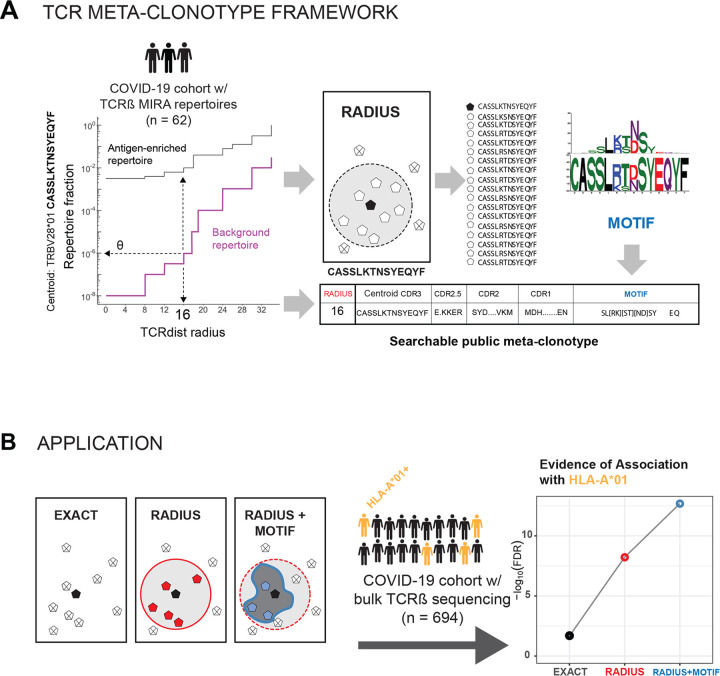
Figure 1. TCR meta-clonotype framework and application.
(A) Framework: antigen-enriched repertoires were used together with antigen-unenriched background repertoires to engineer TCR meta-clonotypes that define biochemically similar TCRs based on a centroid TCR and a TCRdist radius. Antigen-enriched TCRs came from CD8+ T cells activated by SARS-CoV-2 peptides that were previously discovered (Nolan et al., 2020) in 62 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 using MIRA (Multiplex Identification of Antigen-Specific T Cell Receptors Assay, Klinger et al., 2015). With each clonotype from the antigen-enriched TCRs, we used tcrdist3 to evaluate the repertoire fraction spanned at different TCRdist radii within (i) its antigen-enriched repertoire (black) and (ii) a control V- and J-gene matched, inverse probability weighted background repertoire (purple). The set of antigen-enriched TCRs spanned by the optimal radius were then used to develop an additional meta-clonotype motif constraint based on conserved residues in the CDR3 (see Methods for details). An example logo plots shows the CDR3 β-chain motif formed from TCRs – activated by a SARS-CoV-2 peptide (MIRA55 ORF1ab amino acids 1316:1330, ALRKVPTDNYITTY) – within a TCRdist radius 16 of this meta-clonotype’s centroid. (B) Application: TCR meta-clonotypes were used to quantify the frequency of putative SARS-CoV-2 antigen-specific TCRs in a large diverse cohort, from whom bulk TCR repertoires were collected 0–30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (n=694). Meta-clonotypes were evaluated based on their association with a restricting HLA allele. In most cases, evidence of HLA-restriction was stronger for meta-clonotypes (RADIUS or RADIUS+MOTIF) compared to using exact matches to the centroid TCR (EXACT), demonstrated by lower false-discovery rate (FDR) adjusted q-values and larger HLA regression coefficients in beta-binomial count regression models that account for sequencing depth and control for patient age, sex, and days from diagnosis.