Figure 5.
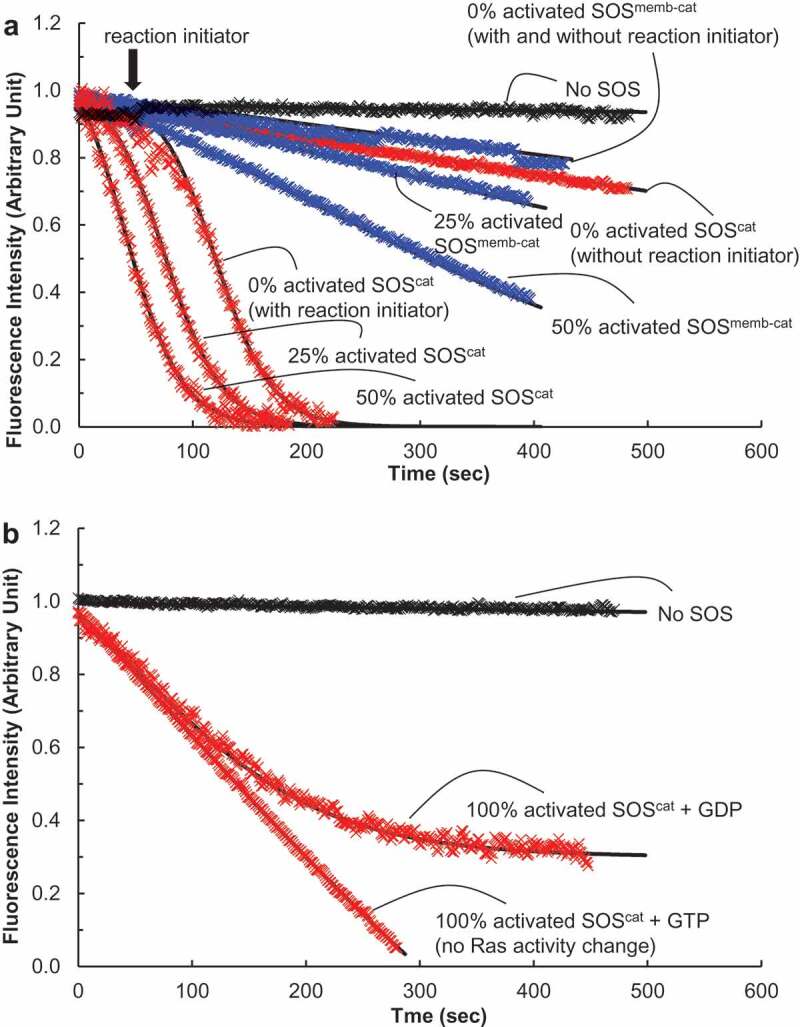
Autoactivation of SOS with solution Ras. We performed fluorescence mant-based Ras activation and inactivation assays on the catalytic activity of SOScat (in red) or SOSmemb-cat (in blue) for the Ras solution. The assay buffer for this analysis consisted of 5 mM MgCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, and 10 mM TrisHCl (pH 7.4). (a). The Ras activation assay was initiated by addition of the various forms of SOScat or SOSmemb-cat (1 μM) to an assay cuvette containing the solution wt Ras that is preloaded with mant fluorescence-tagged GDP* (wt Ras•GDP*, 1 μM) in the presence of excess GTP (1 mM) in an assay buffer. This assay produces wt Ras•GTP (Ras activation). We used a LS 55 Fluorescence Spectrometer (excitation wavelength of 360 nm and emission wavelength of 440 nm) to monitor the change in the mant fluorescence by the SOS-mediated displacement of the wt Ras•GDP* with the abundant free GTP to produce wt Ras•GTP. When necessary, as indicated by an arrow, an autoactivation reaction initiator wt Ras•GTP (0.1 μM, final concentration) was added over the course of the assay with 0% activated SOS. The fraction of the partly activated SOS (e.g. 25% activated SOS, see the Materials and Methods section for its preparation) is equivalent to the reaction initiator wt Ras•GTP for initiation of SOS autoactivation. Therefore, for the assay with the partly activated SOS, we omitted use of the reaction initiator wt Ras•GTP. All the data were fit to Equation (1), and the k values of 0% activated SOScat (without the reaction initiator), 0% activated active SOScat (with the reaction initiator), 25% activated SOScat, and 50% activated SOScat were estimated, respectively, as >1700, 117, 78, and 42 s. The k values of 0% activated SOSmemb-cat (without the reaction initiator), 0% activated SOSmemb-cat (with the reaction initiator), 25% activated SOSmemb-cat, and 50% activated SOSmemb-cat also were estimated, respectively, as >20,000, >20,000, 629, and 346 s. (b). The Ras inactivation assay was initiated by the addition of 100% activated SOScat (1 μM) to an assay buffer. The LS 55 Fluorescence Spectrometer was also used to monitor the change in the mant fluorescence by the SOS-mediated displacement of the solution wt Ras preloaded with mant fluorescence-tagged GTP* (wt Ras•GTP*, 1 μM) with the abundant free GDP (1 mM) in the assay buffer to produce wt Ras•GDP (Ras inactivation). As a control, an abundant free GTP (1 mM) instead of the abundant free GDP (1 mM) was used. The catalytic action of SOS on wt Ras•GTP* with the abundant free GTP that produces wt Ras•GTP does not change Ras activity (both of the substrate wt Ras•GTP* and the product wt Ras•GTP are the same active Ras). Therefore SOS action on this control experimental condition results in Ras activity preservation (no Ras activity change)
