Figure 4.
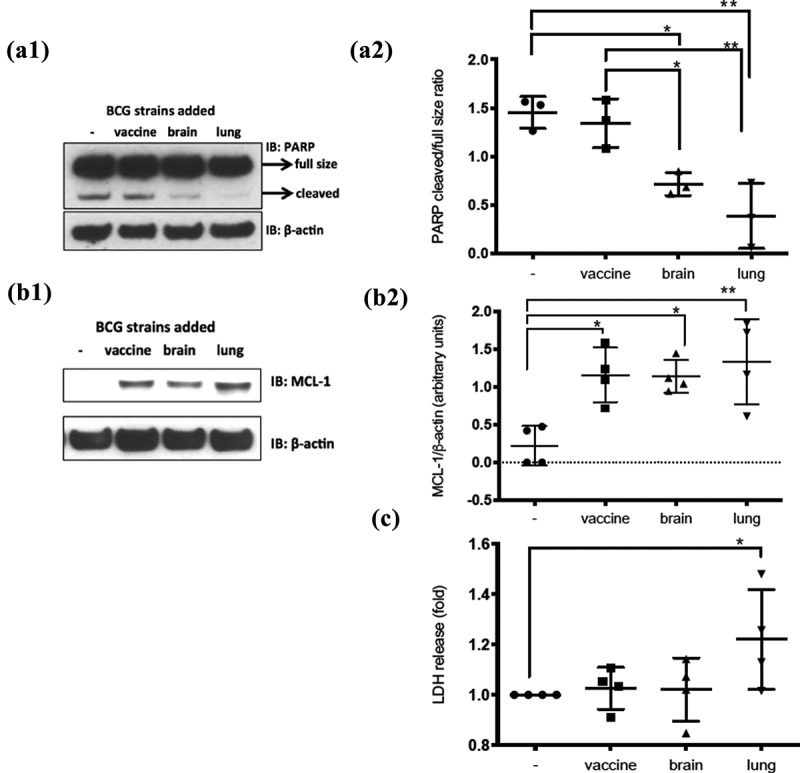
Diminished apoptosis on infected cells by BCG-lung and BCG-brain strains and higher necrosis by infection with BCG-lung measured by LDH-release
(A1) Cells infected with BCG-brain and BCG-lung strains show markedly reduced apoptosis. dTHP1 cells were not infected or infected with the three different strains of BCG (MOI 2) for 2 d. Protein lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis and proved for PARP and β-actin. Blot shown is representative of three repetitions and (A2) Graph is the cumulative densitometric analysis of the ratio of cleaved PARP over the full-size protein. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ANOVA). (B1) Monocyte-derived macrophages infected at MOI of two with the three strains for 2 d showed higher MCL-1 expression with a trend of higher expression on the lung strain infected cells, blot representative of four repetitions, represented in (B2) Graph, is the cumulative densitometric analysis of MCL-1 levels normalized to actin levels (MCL-1/β-actin). Data, mean ± SD (n = 4; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; ANOVA). (C) Necrosis is augmented on dTHP1 cells infected with the BCG-lung strain. The supernatants of dTHP1 cells non-infected or infected with the three strains of BCG at a MOI of 2 were used to quantify the release of LDH from the cells. LDH release is expressed as fold increases when compared to the non-infected condition (arbitrarily defined as “1”). LDH levels were elevated in BCG-lung. Data, mean ± SD (n = 4; *p < 0.05; ANOVA)
