Figure 2.
Arf4 α3 helix, which participates in rhodopsin interactions, is evolutionary conserved, with the exception of mouse and rat
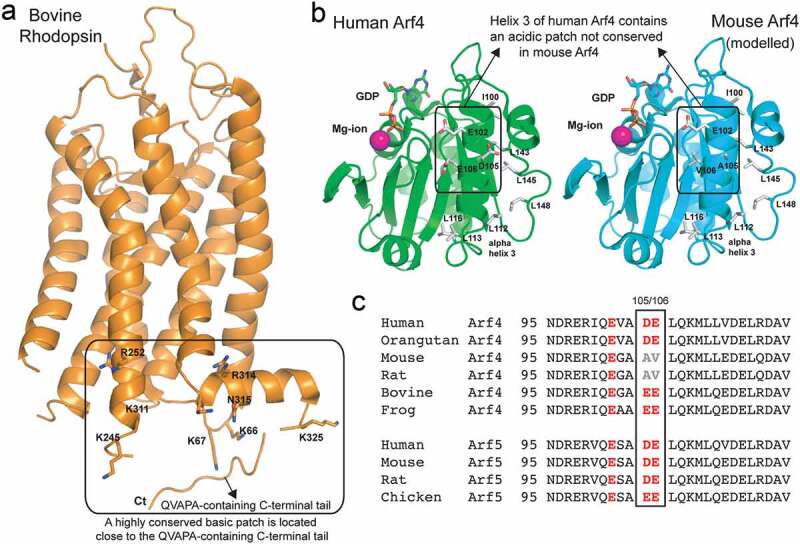
(a) The crystal structure of bovine rhodopsin (PDB code 1F88) is shown in orange cartoon representation. Residues forming a basic patch near the C-terminal tail are shown in stick representation and labelled according to the bovine sequence. The position of the C-terminal QVAPA tail is indicated (note that the linker connecting the C-terminal tail to the rhodopsin core domain was not resolved in the crystal structure). (b) Crystal structure of human Arf4 (PDB code 1Z6X) is shown as a green cartoon representation and that of mouse Arf4 (modelled based on the human Arf4 structure) as a cyan cartoon representation. GDP (sticks) and a magnesium ion (pink ball) mark the GTPase active site of Arf4. Residues forming the acidic patch on human Arf4 and neighbouring hydrophobic residues are shown as sticks and labelled according to the sequence. (c) Sequence alignment of the region corresponding to helix 3 of Arf4 and Arf5 and the surrounding residues, from different species. The acidic residues substituted with hydrophobic residues in mouse and rat Arf4 are boxed.
