Figure 1.
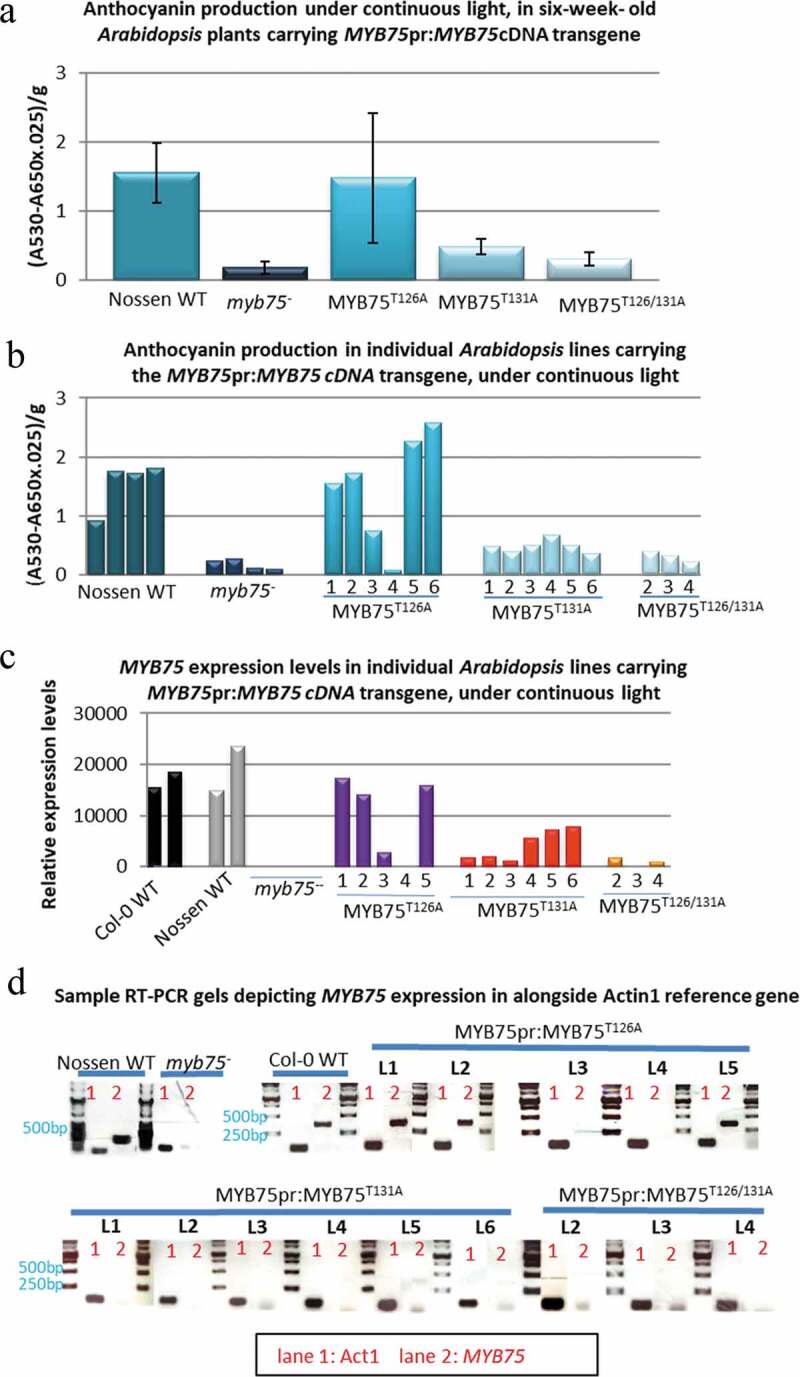
Complementation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis myb75− null mutants (Nossen), by different MYB75 phosphovariants, driven by the endogenous MYB75 promoter. The ability of each phosphovariant to complement anthocyanin production in myb75− mutants was evaluated in 6-week-old heterozygous T2 plants, exposed to continuous light, for over 48 h. Total anthocyanin (average for each genotype) was quantified as described in materials and methods, error bars represent ±SD. (a) Anthocyanin production was recovered in MYB75pr:MYB75T126A genotype, but not in MYB75pr:MYB75T131A or MYB75pr:MYB75T126/131A mutants. (b) Examination of anthocyanin levels in individual lines revealed that only lines 1,2,5 and 6 from MYB75pr:MYB75T126A genotype produced anthocyanin levels comparable to Nossen WT. (c) Gene expression analysis, by semi-quantitative RT PCR revealed that transgenic lines which showed anthocyanin complementation were expressing recombinant MYB75 at levels comparable to wild type plants, while lines that failed to produce WT levels of anthocyanin had negligible levels of recombinant MYB75 expression. (d) Sample gels of RT-PCR results depicting expression of MYB75 in different MYB75pr:MYB75 lines, along with Nossen WT, myb75−, and Col-0 WT controls. Lane1-Actin1 control, Lane2-MYB75.
