Figure 2.
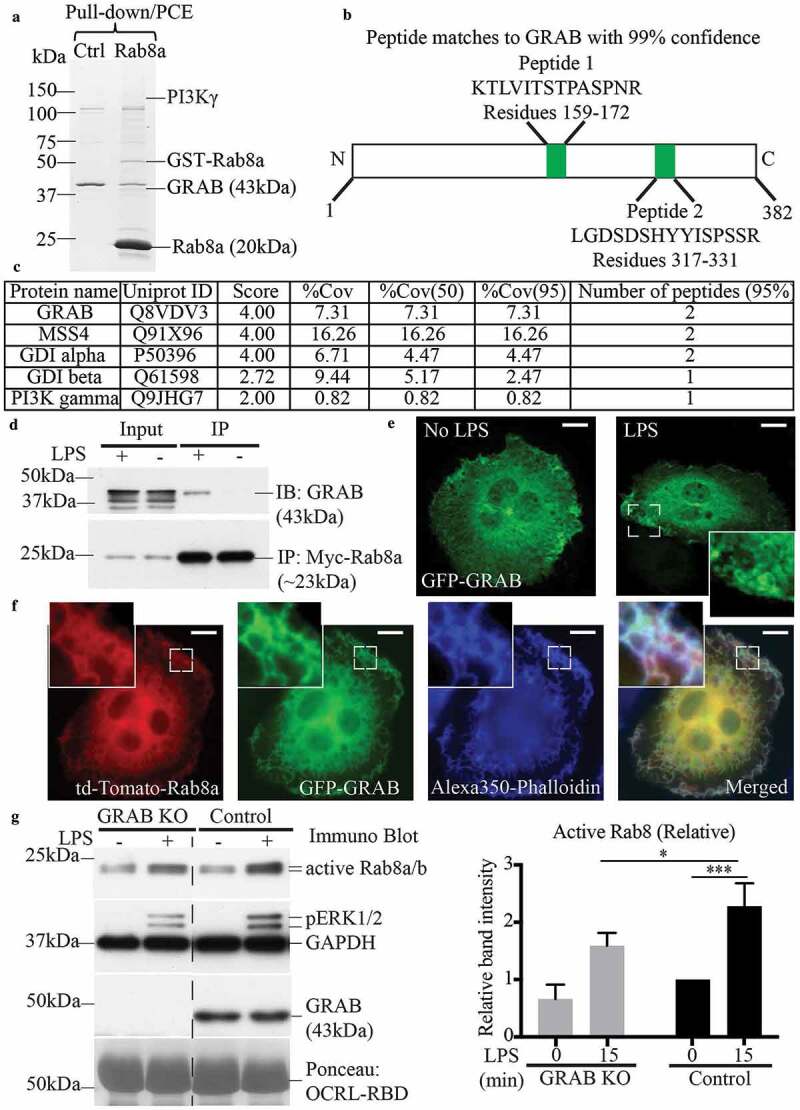
GRAB interacts with Rab8a in an LPS dependent manner for its GEF activity. GSH-Sepharose beads with bound GST-Rab8a were used to pull-down proteins from LPS-treated (30 mins) RAW 264.7 cell lysate and eluted with proteases. The elutes were separated on a 7–15% SDS-PAGE gradient gel. (a) A faint band between 150 kDa and 100 kDa indicating the presence of previously identified effector PI3Kγ and another band above 37 kDa was identified as the Rab8a GEF GRAB (~43kDa), both of which were absent in the GST control sample. Mass spectrometry analysis identified two trypsin-digested peptides from GRAB with 95% confidence. (b) Schematic of peptide sequences of GRAB identified from the mass spectrometry. (c) Example list of identified known Rab8a interacting proteins from the mass-spectrometry analysis. (d) Immunoprecipitation of GRAB using anti-myc antibodies from cell lysates of Rab8a KO cells ± LPS (30 min) reconstituted with myc-Rab8a. Fluorescence microscopy images of fixed LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells transiently overexpressing either (e) GFP-GRAB or (f) co-expressing td-Tomato-Rab8a and GFP-GRAB and stained with Alexa350-phalloidin. Scale bars, 10 µm. (g) Immunoblotting for levels of GTP-Rab8 pulled-down from the lysate of control and GRAB KO cells ± LPS (100 ng/ml, 15 min) using GSH-Sepharose beads with GST-OCRL-RBD. Levels of active Rab8 were quantified by using the densitometric ratio between the band intensities of captured Rab8 and GAPDH. Significance was measured via two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, n = 3)
