Fig 6.
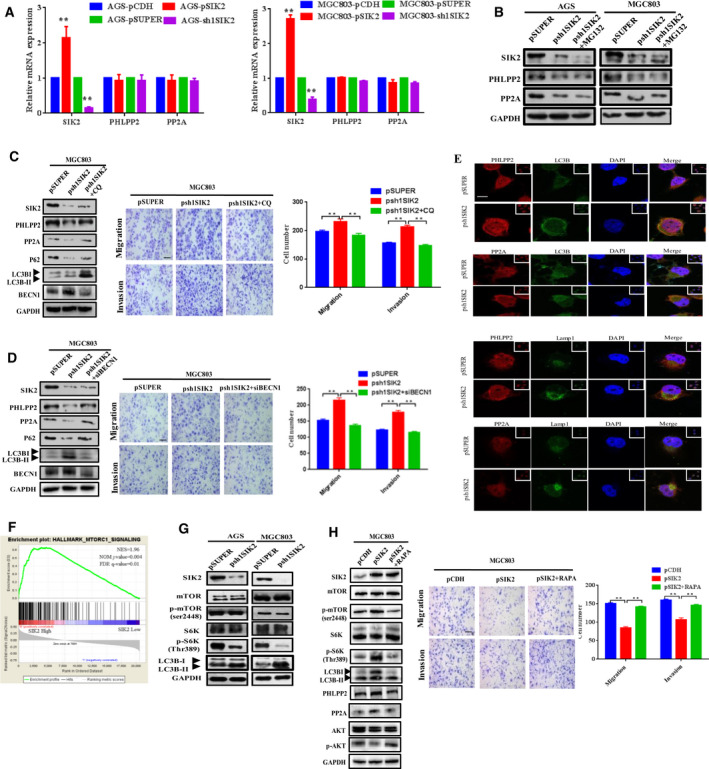
SIK2 inhibits mTORC1‐dependent autophagic degradation of PHLPP2 and PP2A. (A) The mRNA expression levels of PHLPP2 and PP2A in the SIK2‐overexpressed or ‐knockdown AGS and MGC803 cells assessed by qRT‐PCR. (B) Effect of proteasome inhibitor MG132 (5 μm, 24 h) on the expression of PHLPP2 and PP2A in the SIK2‐knockdown AGS‐psh1SIK2 and MGC803‐psh1SIK2 cells. (C,D) Effect of the autophagy inhibitor CQ (C) or knockdown of Beclin‐1 (BECN1) (D) on the expression of PHLPP2, PP2A and autophagic markers in the SIK2‐knockdown MGC803‐psh1SIK2 cells, and the cell migratory and invasive abilities. Scale bar = 200 µm. (E) Immunostaining analysis of colocalization of PHLPP2 or PP2A with LC3B and LAMP1 in MGC803‐psh1SIK2 and the control cells. Cells were fixed and labeled with anti‐PHLPP2 or anti‐PP2A (green) and anti‐LC3B or anti‐LAMP1 (red) antibodies. Yellow = merge/colocalization. White boxes in the images are pictures of the area of the cells taken with low magnification. Scale bar = 10 µm. (F) Analysis of the mTORC1 signal enrichment scores between SIK2 high and low expression groups according to the TCGA stomach cancer dataset using the GSEA program. (G) Western blot analysis of the expression of autophagy signaling molecules in the SIK2‐knockdown AGS‐psh1SIK2 and MGC803‐psh1SIK2 cells. (H) Effect of addition of mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (100 ng·mL−1, 6 h) in the SIK2‐knockdown MGC830 cells on the expression of autophagy markers and AKT phosphorylation as well as the cell migratory and invasive abilities. Scale bar = 200 µm. Data are expressed as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments with triple replicates per experiment. **P < 0.01.
