Fig. 4.
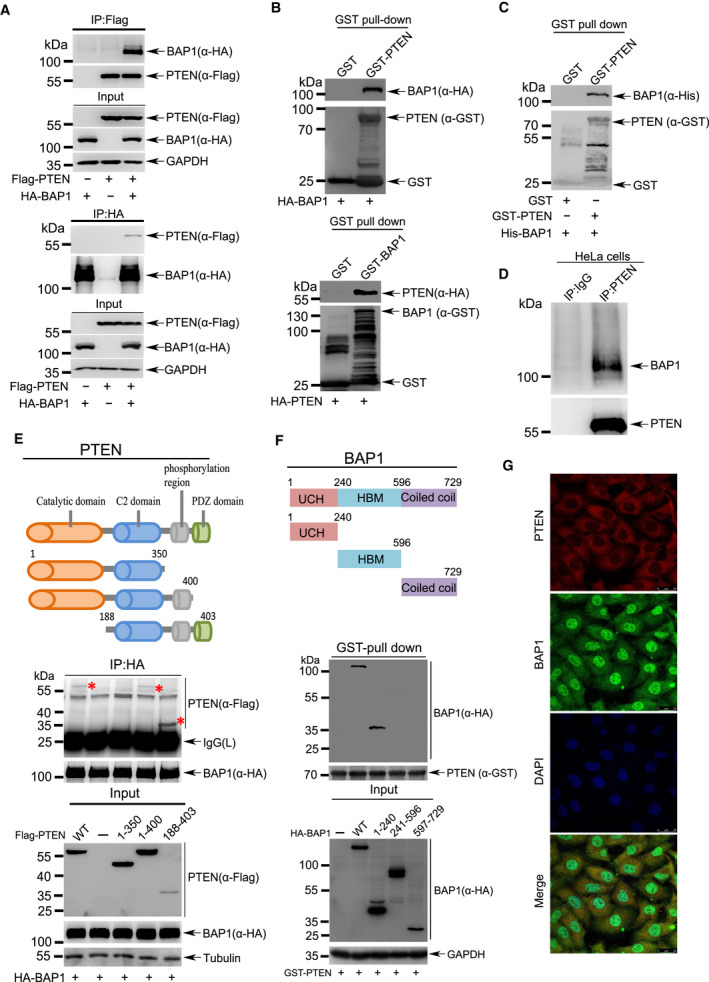
BAP1 directly interacts with PTEN. (A) Lysates from 293T cells transfected with Flag‐PTEN or/and HA‐BAP1 were immunoprecipitated with anti‐Flag antibody, and then immunoblotted with anti‐HA antibody. The reciprocal immunoprecipitation was also conducted to validate the interaction. (B) Purified GST‐PTEN or GST‐BAP1 was incubated with lysates from 293T cells expressing HA‐BAP1 or HA‐PTEN, respectively, for pull‐down assay of protein–protein interaction. (C) GST‐fusion protein pull‐down assay with purified GST‐PTEN and His‐BAP1. (D)The interaction between endogenous BAP1 and PTEN. Lysates from HeLa cells was used for Co‐IP with anti‐PTEN antibody, and followed by western blotting analysis with anti‐BAP1 antibody. Anti‐immunoglobulin (IgG) served as the negative control. (E) Upper panel, a series of truncated forms of Flag‐PTEN were generated based on its domains including a catalytic domain, a C2 domain, a multisite phosphorylation domain, and a PDZ‐binding domain. Middle panel, lysates from 293T cells transfected with HA‐BAP1 full‐length or truncated Flag‐PTEN were co‐immunoprecipitated with anti‐HA antibody, and followed by western blotting analysis with anti‐Flag antibody. Lower panel, immunoblotting was performed for Input. (F) Upper panel, a series of truncated forms of HA‐BAP1 were generated based on its domains including an ubiquitin C‐terminal hydrolase domain (UCH), a HCF‐binding motif (HBM), and a coiled‐coil domain with two nuclear localization sequences (NLS) at its C terminus. Middle panel, lysates from 293T cells transfected with full‐length or truncated HA‐BAP1 were incubated with bacterially produced GST‐PTEN for GST pull‐down assays in vitro. Lower panel, immunoblotting was performed for Input. (G) Colocalization of PTEN and BAP1 in DU145 cells stably expressing PTEN. Scale bars: 25 μm. All above experiments were repeated at least 3 times.
