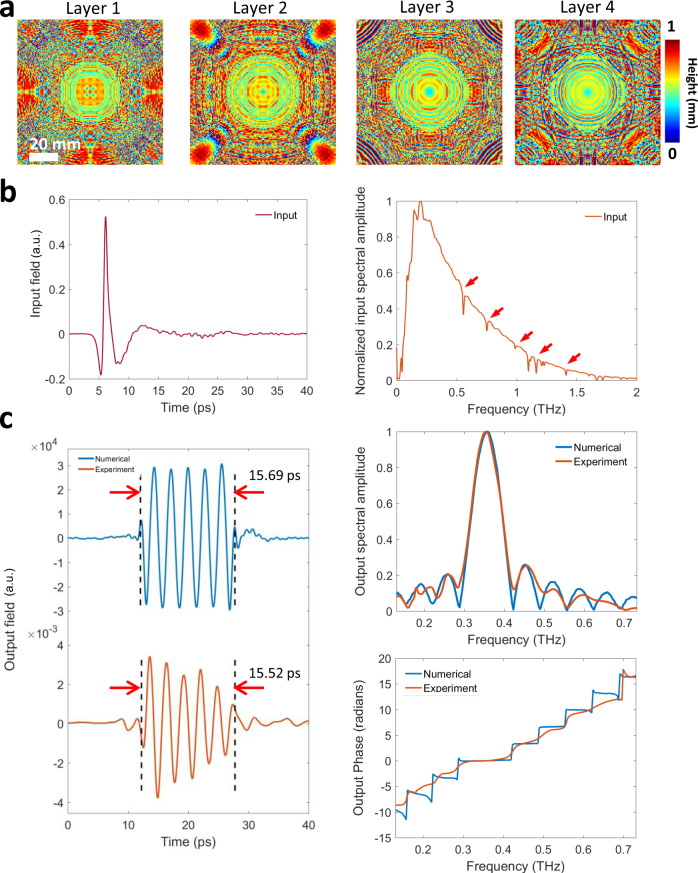
Fig. 2. Pulse shaping diffractive network design and output results.
a The thickness profiles of the resulting diffractive layers after deep learning-based training in a computer. These diffractive layers synthesize a square pulse with a width of 15.69 ps over the output aperture for an input pulse shown in b. b Normalized input terahertz pulse measured right after the input aperture (see Fig. 1); in time-domain (left) and spectral domain (right). The red arrows on the measured spectral amplitude profile represent the water absorption bands at terahertz frequencies. c Left: The numerically computed (blue) and the experimentally measured (orange) output pulses in time domain. Top right: The normalized spectral amplitudes corresponding to the numerically computed (blue) and the experimentally measured (orange) pulses. Bottom right: Unwrapped spectral phase distributions computed based on the numerical forward model (blue) and the experimentally measured (orange) pulse.