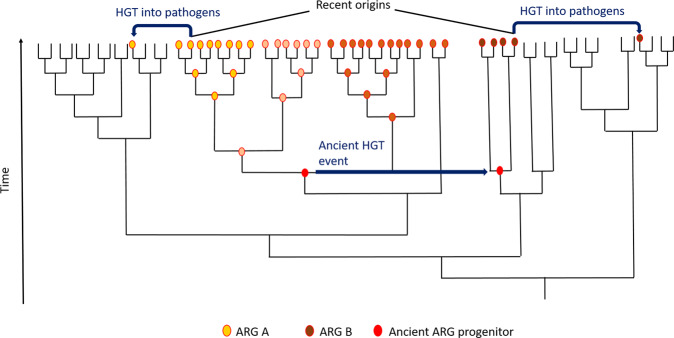
Fig. 2. The principle of recent origins.
Schematic phylogeny illustrating the principle of recent origins of ARGs. Blue arrows represent horizontal gene transfer events (HGT); red circle on node represents an ARG progenitor. Changing color of circle represents sequence evolution over time. Two possible scenarios are shown: ARG A evolves in the same taxonomic clade as the ARG progenitor prior to being transferred to a pathogen. In case of ARG B, the ARG progenitor is acquired through an ancient HGT event before it is, more recently, transferred to pathogens, and is thus not present in the sister clades of the recent origin of ARG B. In both cases, the recent origin is the taxon from which the gene is mobilized into clinically relevant contexts.