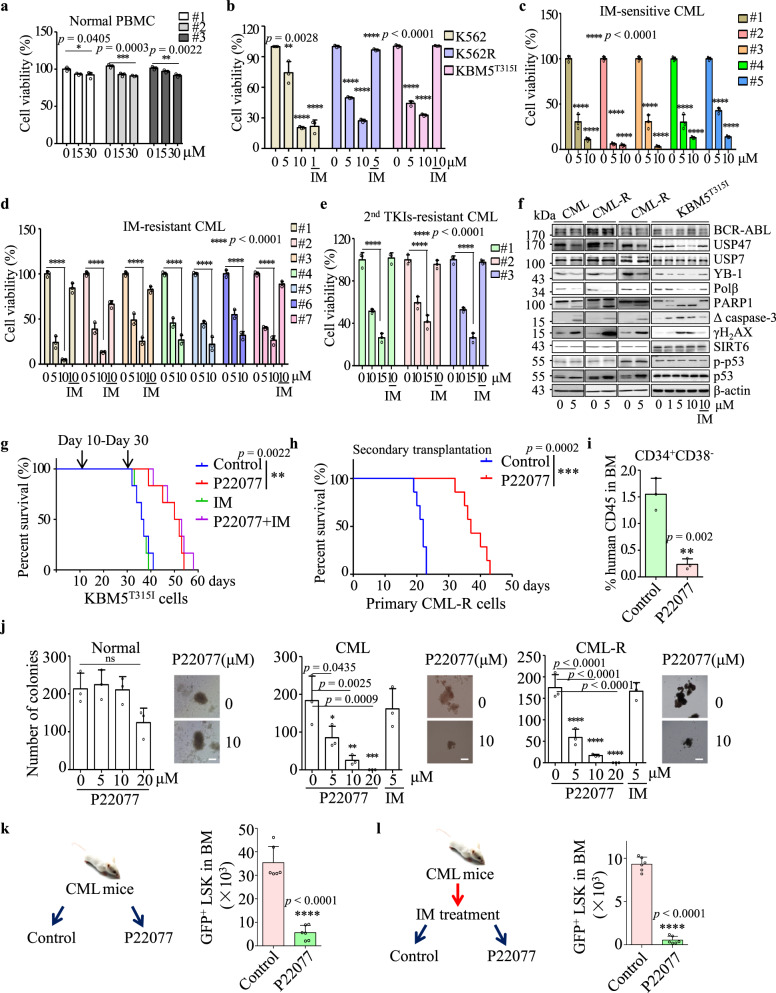
Fig. 7. P22077 shows remarkable toxicity on CML cells and CML leukemia stem/progenitor cells in vitro and in vivo.
a–e Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from normal donors (a) (n = 3 samples examined over three independent experiments), CML cell lines (b) (n = 3 cells examined over three independent experiments), and BM mononuclear cells from IM-sensitive (c) (n = 5 samples examined over three independent experiments) and IM-resistant (d) (n = 7 samples examined over three independent experiments) CML patients were treated with different concentrations of P22077 or IM for 48 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK8 assay. e BM mononuclear cells resistance to the second-generation TKIs (dasatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib) from CML patients were treated with P22077 and IM for 48 h (n = 3 samples examined over three independent experiments). Cell viability was measured by CCK8 assay. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. p-values were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. f Primary CML (IM-sensitive), CML-R (IM-resistant) BM mononuclear cells and KBM5T315I cells were treated with P22077 for 48 h. Cell lysates from the indicated cells were extracted and subjected to immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. g P22077 (30 mg/kg/day), IM (50 mg/kg/day), P22077 (30 mg/kg/day) in combination with IM (50 mg/kg/day) or vehicle were given to mice transplanted with KBM5T315I cells by intraperitoneal injection (n = 6 biologically independent samples per group) from day 15 to day 30. **p < 0.01, by Mantel-Cox-log-rank test. h, i Human CD45 cells from CML BM (patient-derived xenograft model) were transplanted into two groups of B-NDG mice. The survival time of the mice (h) (n = 7 biologically independent samples per group) was determined, and the percentages of CD34+CD38− cells in human CD45 cells (i) (n = 3 biologically independent samples per group) from BM were measured. Data are mean ± s.d. p-values were analyzed by Mantel-Cox-log-rank test (h) and two-sided Student’s t-test (i). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. j CD34+ cells derived from normal (n = 3 samples examined over three independent experiments), primary IM-sensitive CML (n = 3 samples examined over three independent experiments), and primary IM-resistant CML BM mononuclear cells (n = 3 samples examined over three independent experiments) were treated with different concentrations of P22077. The colonies were counted on day 14. Scale bars, 100 μm. Data are mean ± s.d. p-values were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns no significant. k Wild-type mice received BCR-ABL retroviral transplantation for 21 days, and the mice were treated with control or P22077 by intraperitoneal injection for 14 days. GFP+LSK cells from the BM of the two groups (n = 6 biologically independent samples per group) were evaluated by FACS. Data are mean ± s.d. p-values were analyzed by two-sided Student’s t-test. ****p < 0.0001. l Wild-type mice received BCR-ABL retroviral transplantation for 21 days, and the mice were treated with IM for 40 days. Mice were divided into two groups (n = 6 biologically independent samples per group). One group received P22077, and the other group received the vehicle and used as the control. After 12 days, the number of GFP+LSK cells in the BM of the mice was examined. Data are mean ± s.d. p-values were analyzed by two-sided Student’s t-test. ****p < 0·0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.