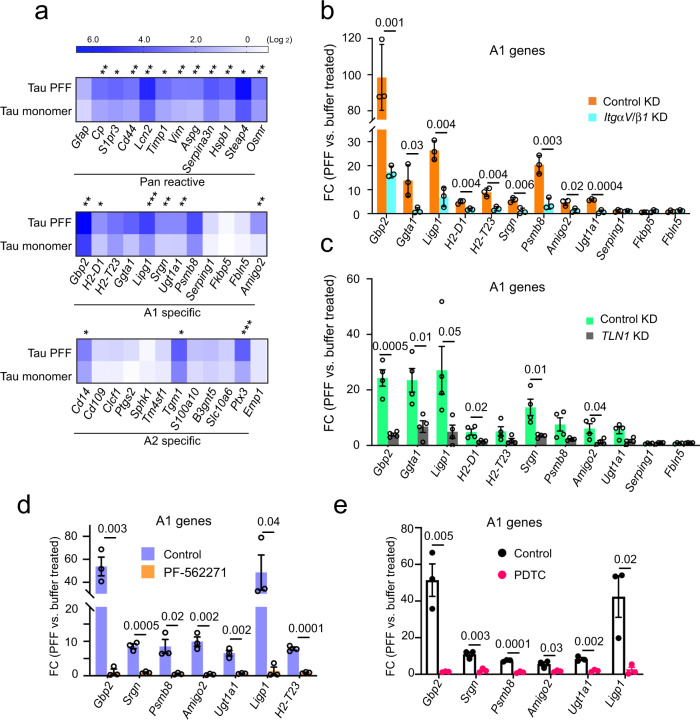
Fig. 6. Tau PFF converts astrocytes to a neurotoxic state in an integrin-dependent manner.
a A heat map shows the expression of pan-reactive, A1 and A2 signature genes in Tau monomer- and PFF-treated primary astrocytes (200 nM, 6 h), which is normalized to PBS-treated cells. Shown is the average of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate p value (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001) from two-tailed unpaired t-test. b The expression of the indicated A1 genes were analyzed by qRT-PCR from PBS- or Tau PFF-treated (200 nM, 6 h) astrocytes, which had been infected with lentiviruses (72 h) expressing control or ITGαV/β1 shRNAs. Fold changes (FC) were normalized to PBS-treated samples. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments each with two technical duplicates. c As in b, except that immunopurified astrocytes infected with control-expressing or Talin1 (TLN1) shRNA-expressing lentiviruses were used. Mean ± SEM, n = 4 biologically independent samples. d As in c, except that cells were treated with DMSO or PF-562271 (1 μM, 1 h) instead of lentivirus prior to PBS or Tau PFF treatment. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 biologically independent samples, each with two technical duplicates. e Tau PFF-induced A1 genes is suppressed by a NFκB inhibitor. As in d, except that cells were treated with PDTC (90 μM) for 1 h before Tau PFF and PBS treatment. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 biologically independent samples. The numbers above indicate p value determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test.