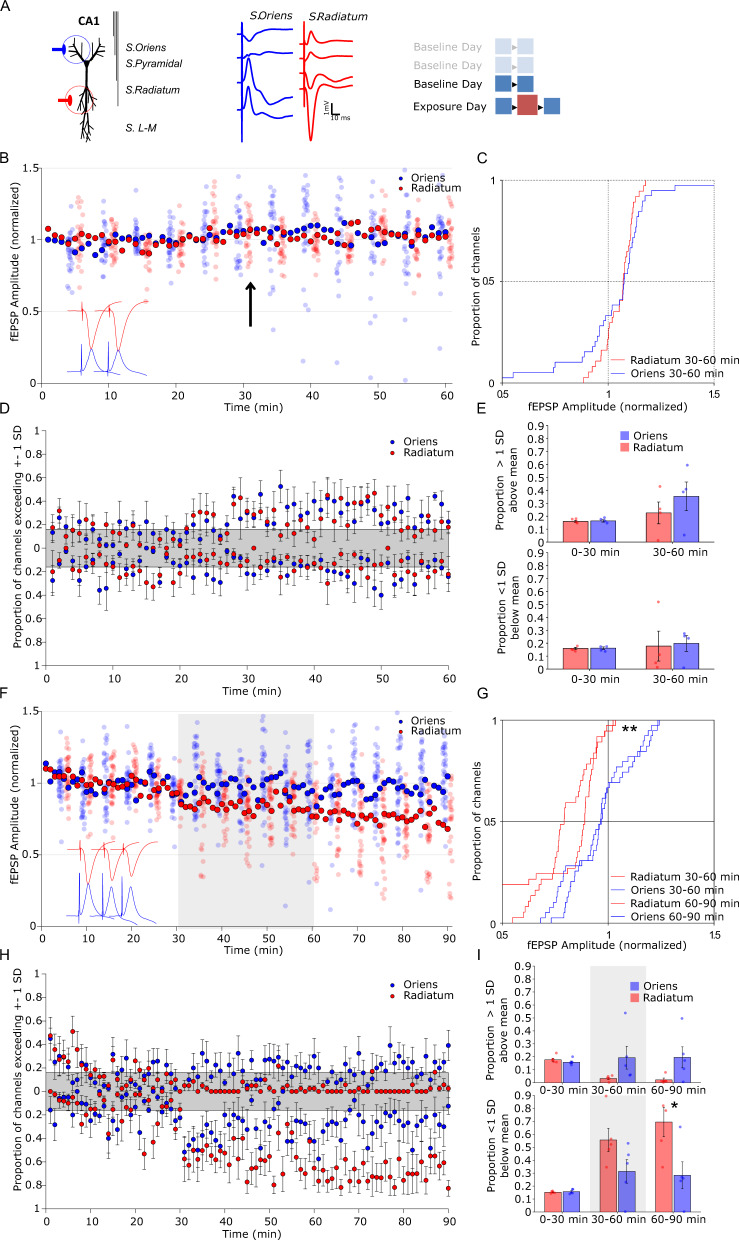
Fig. 1. Exposure to a novel environment elicits a decrease in fEPSP specific to stratum radiatum stimulation.
A Each tract was composed of four electrodes that spanned the laminar extent of CA1. Two stimulation electrodes were positioned to activate schaffer collateral inputs to either basal or apical CA1 dendrites in the stratum oriens or stratum radiatum respectively. Stratum oriens stimulation evoked a negative going potential in superficial electrodes and a positive going potential in deep electrodes, whereas stratum radiatum stimulation did the opposite. Three baseline days preceded the novel environment exposure day, wherein the familiar environment was presented before and after the novel environment. B On the final baseline day evoked field potentials are stable. Two 30-min recordings in a familiar recording chamber were separated by a brief handling episode (arrow). Solid marker indicates the cross-channel average, while each channel is plotted every 5 stimulations and offset for clarity. Hippocampal CA1 field potentials evoked from stimulation of the oriens or radiatum pathway showed no significant change across time. C Cumulative distribution of evoked field potential change in the second 30-min epoch relative to the first (blue, oriens, n = 38 channels; red, radiatum, n = 38 channels). D Per-animal proportion of channels exceeding 1 standard deviation of the channel’s baseline variance at each stimulation. Shaded area represents the proportion of channels expected to be above or below 1 standard deviation based on a normal distribution (n = 5 rats). E Proportion of channels exceeding 1 standard deviation above (top graph) or below (bottom graph) baseline, in 30-min bins. No significant change in distribution was observed on the baseline day in either channel (n = 5 rats). F On the exposure day, A 30-min baseline recording was followed by 30 min in a novel environment (gray shading), followed again by 30 min in the familiar recording chamber. Solid marker indicates the cross-channel average, while each channel is plotted every 5 stimulations and offset for clarity. G Cumulative distribution of amplitude change relative to baseline period during novelty (solid) and after returning to the familiar chamber (dashed) showed a widespread decrease in radiatum evoked field potential distributions relative to the oriens pathway (blue, oriens, n = 38 channels;red, radiatum, n = 38 channels). H Per-animal proportion of channels exceeding 1 standard deviation of the channel’s baseline variance at each stimulation (n = 5). I Proportion of channels averaged in each epoch indicate a specific increase in the proportion of channels lower than 1 standard deviation from baseline in the radiatum channel after exposure to the novel environment (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 follow-up t-test (two-way) comparison between treatment group for epochs after significant group by epoch ANOVA interaction, and k-s test for distribution. Error bars represent ± SEM.