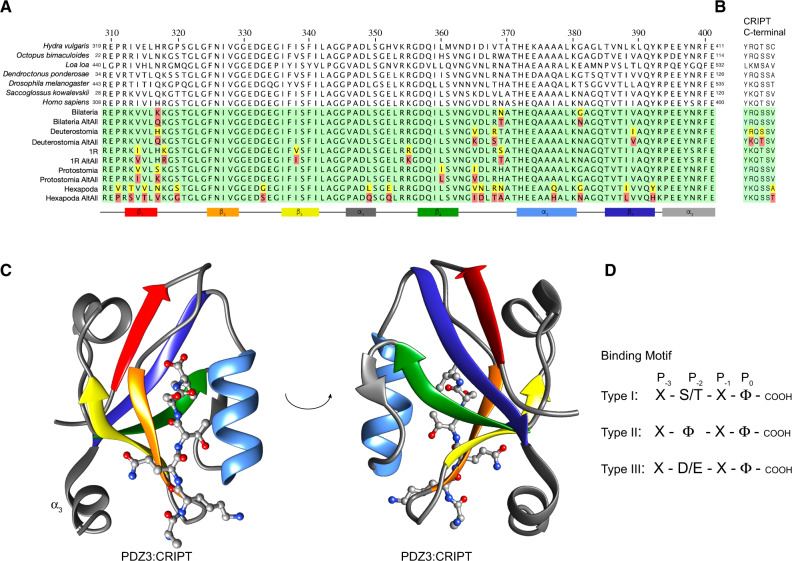
Fig. 1.
Extant and reconstructed ancient DLG PDZ3 and CRIPT sequences. (A) Alignment of DLG PDZ3 sequences. The sequence numbering of extant PDZ3 domains refers to the full-length DLG protein from the respective species. For simplicity, we use numbering of PDZ3 according to the human DLG4 sequence throughout the article. In the alignment of ancestral sequences (green background), residues with posterior probabilities <0.5 (red) and >0.5 but <0.8 (yellow) are highlighted. The secondary structure is from the crystal structure of DLG4 PDZ3 depicted in panel (C) with the corresponding color code. (B) Alignment of C-terminal CRIPT sequences. (C) Crystal structure of human DLG4 PDZ3 in complex with a CRIPT peptide (YKQTSV) (PDB ID: 5HEB). Secondary structure elements are marked in accordance with the alignment in panel (A). The structure was visualized using UCSF Chimera software. (D) Illustration of three common C-terminal PDZ-binding motif types. X, any amino acid residue; Φ, hydrophobic residue. Previous studies have shown that human DLG4 PDZ3 prefers a type I motif with a Val at position P0.