FIGURE 1.
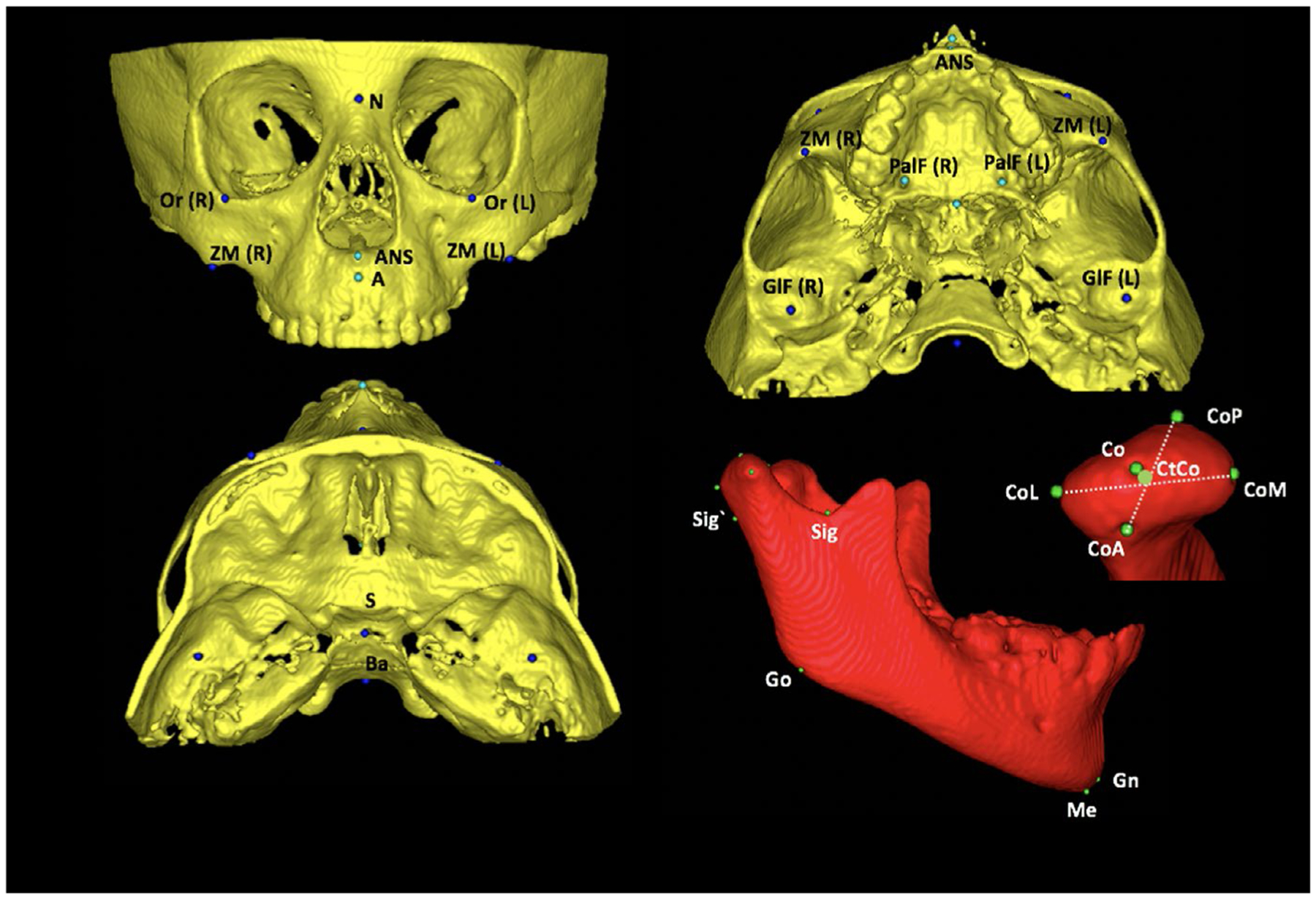
Anatomical landmarks used in measurement’s method. A, Landmarks of measurement’s method: orbitale (Or): most inferior point at the inferior contour of the orbit; zygomaticomaxillary (ZM): most inferior point at the zygomatic maxillary suture; anterior nasal spine (ANS): most anterior point at the anterior nasal spine; palatine foramen (PalF): the middle and inferior point at the palatine foramen; GlF (glenoid fossa): most superior point at the glenoid fossa; sella (S): midpoint at the sella turcica; basio (Ba): most inferior point at the anterior border of magnun foramen; 2-D: mandibular landmarks: condilium (Co): most superior point on the curvature of the condylar head; anterior pole (CoA): most anterior point of the condylar head; posterior pole (CoP): most posterior point of the condylar head; medial pole (CoM): most medial point of the condylar head; lateral pole (CoL): most lateral point of the condylar head; centre of condyle (CtCo): centre point on the line connecting the centres of latero-medial and antero-posterior distances, sigmoid posterior (Sig`): most posterior point of the projection of sigmoid notch point using a line parallel to Frankfurt plane; gonion (Go): midpoint of the angle of the mandible determined by bisecting the angle formed by the mandibular plane and the adjacent line to mandibular ramus; gnathion (Gn): most anteroinferior and midline point on the contour of the bony chin symphysis, determined by bisecting the angle formed by the mandibular plane and a line through pogonion and nasion; and menton (Me): most inferior midline point on the mandibular symphysis
