Fig. 1.
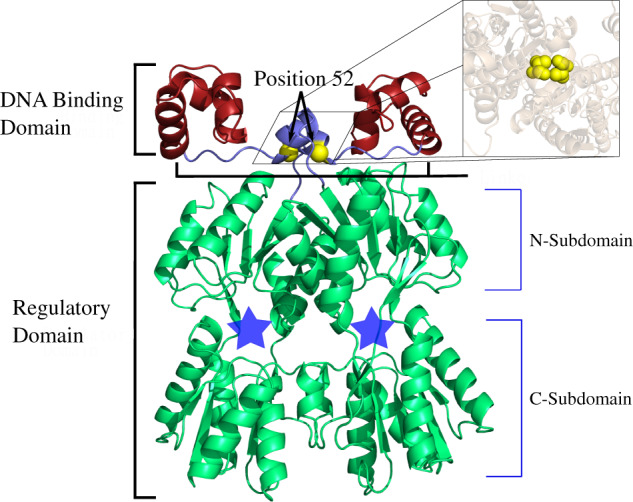
LacI structure (pdb ID 1efa [Bell and Lewis 2000]) colored and labeled by domain. The minimal LacI structure for high affinity DNA binding is a homodimer (reviewed in Swint-Kruse and Matthews [2009]). Each monomer comprises two major domains—a DNA-binding domain (red) and a -regulatory domain (green)—that are connected by a flexible linker region (blue). DNA-binding involves positions on the top surface of the DNA-binding domains as well as several linker positions. The Cα’s of linker position 52 are highlighted with yellow spheres; the inset shows a top-down view of both V52 side chains using space-filling spheres. In the regulatory domains, locations of the allosteric effector-binding sites are indicated with blue stars. Small molecule “inducer” binding to this site diminishes DNA-binding affinities by up to 1,000-fold (Swint-Kruse and Matthews 2009). The structure shown and used in this work was extracted from a crystal structure (1efa, Bell and Lewis [2000]) that was determined in the presence of bound DNA and ortho-nitrophenyl-beta-d-fucopyranoside (“ONPF,” an anti-inducer that binds in the allosteric site and enhances DNA binding). This figure was rendered with pyMOL (Schrödinger 2010).
