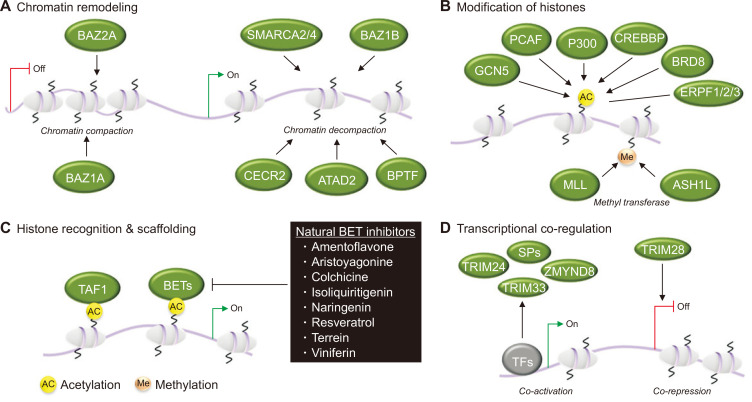
Figure 1. Bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and gene regulation.
(A) BRD-containing proteins are frequently found in chromatin-remodeling complexes. For example, bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain (BAZ) proteins BAZ1A and BAZ2A promote chromatin compaction that leads to gene silencing. Other BRD-containing proteins promote chromatin decompaction, thus enhancing gene transcription. Examples include Switch/sucrose non-fermenting-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A members 2 and 4 (SMARCA2/4) and BAZ1B; cat eye syndrome critical region protein 2 (CECR2); BRD and PHD finger-containing transcription factor (BPTF); and ATPase family AAA domain-containing protein 2 (ATAD2). (B) BRD-containing proteins engage as bi-functional reader-writers in the acetylation and methylation of histones. They include acetyltransferases CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) and E1A-associated protein p300 (EP300), methyltransferases mixed-lineage leukaemia (MLL) and absent small and homeotic disks protein 1-like (ASH1L), or are part of larger histone-modifying complexes that include GCN5-like 2 (GCN5L2; also known as KAT2A), P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF), BRD-containing protein 8 (BRD8) and the BRD and PHD finger-containing proteins (BRPFs), BRPF1, BRPF2 and BRPF3. (C) BRD-containing proteins can serve important roles in transcription by functioning as histone-recognizing scaffolds that promote the assembly of transcriptional complexes. For example, BRD and extraterminal (BET) proteins recruit components of the transcriptional machinery that positively regulate growth-promoting genes. Box: several natural compounds, including resveratrol and naringenin, are known BET inhibitors. Another BRD-containing protein, transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 1 (TAF1), promotes transcription initiation. (D) BRD-containing speckled protein (SP) family members, zinc-finger MYND domain-containing protein 8 (ZMYND8), tripeptide motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) and TRIM33 can serve as transcriptional coregulators, while BRD-containing protein TRIM28 can act as a corepressor. TFs, transcription factors. Adapted from Takao and Panagis, 2017 [34], permission was obtained from the copyright holder.