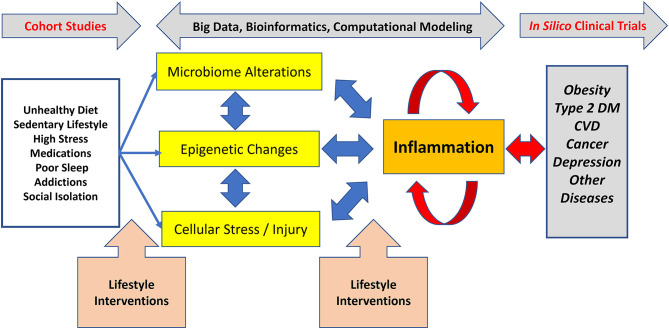
Figure 1.
Lifestyle-associated pathogenesis, interventions, and emerging methods for lifestyle medicine research. Unhealthy lifestyles cause dysregulation in the microbiome, epigenetic changes, and various types of cellular stress and injury which, together, drive inflammation. In turn, inflammation can drive further derangements in the microbiome, can cause distinct epigenetic changes, and can drive further cellular stress and injury. This positive feedback leads to a process wherein inflammation becomes chronic and self-sustaining, ultimately resulting in chronic diseases, such as Type 2 diabetes. The non-linear nature of these processes means that simple reductionist approaches to understanding the connections between lifestyle mismanagement and chronic disease are likely to fail. Effective lifestyle interventions prevent, treat, and reverse common chronic diseases. To accelerate the adoption and dissemination of clinical lifestyle medicine interventions, there is a need for cutting edge biological and computational approaches decipher this complexity. Adapted from Figure 3, Bodai et al. (5) with permission from The Permanente Press.