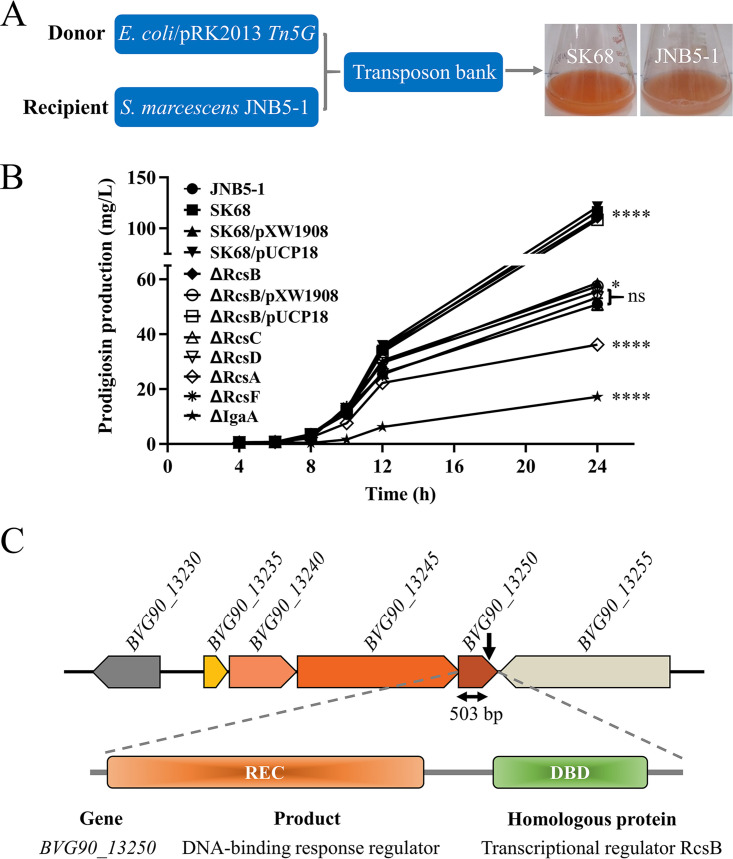
FIG 1.
Regulator RcsB represses prodigiosin biosynthesis in S. marcescens. (A) A prodigiosin-hyperproducing mutant, SK68, was identified by Tn5G transposon insertion mutagenesis. (B) Shake flask fermentation to determine the ability of JNB5-1, SK68, SK68/pXW1908, SK68/pUCP18, ΔRcsB, ΔRcsB/pXW1908, ΔRcsB/pUCP18, ΔRcsA, ΔRcsC, ΔRcsD, ΔRcsF, and ΔIgaA strains to synthesize prodigiosin. JNB5-1 is a wild-type S. marcescens strain, SK68 is an rcsB-disrupted mutant, ΔRcsB is an rcsB deletion mutant, ΔRcsA is an rcsA deletion mutant, ΔRcsC is an rcsC deletion mutant, ΔRcsD is an rcsD deletion mutant, ΔRcsF is an rcsF deletion mutant, ΔIgaA is an igaA deletion mutant, SK68/pXW1908 and ΔRcsB/pXW1908 are rcsB complementary strains with plasmid pXW1908, and SK68/pUCP18 and ΔRcsB/pUCP18 are recombinant strains with empty vector pUCP18. (B) The experiment was performed independently three times. Error bars indicate standard deviations. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to examine the mean differences between the data groups. ****, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05; ns, no significant difference. (C) Genetic loci identified in mutant SK68. (Upper) Genetic map of the disrupted gene BVG90_13250 and its surrounding genes. The transposon insertion site is indicated by the black downward-pointing arrow. (Middle) Domain organization of the BVG90_13250 protein. (Lower) BVG90_13250 is highly homologous to the RcsB protein.