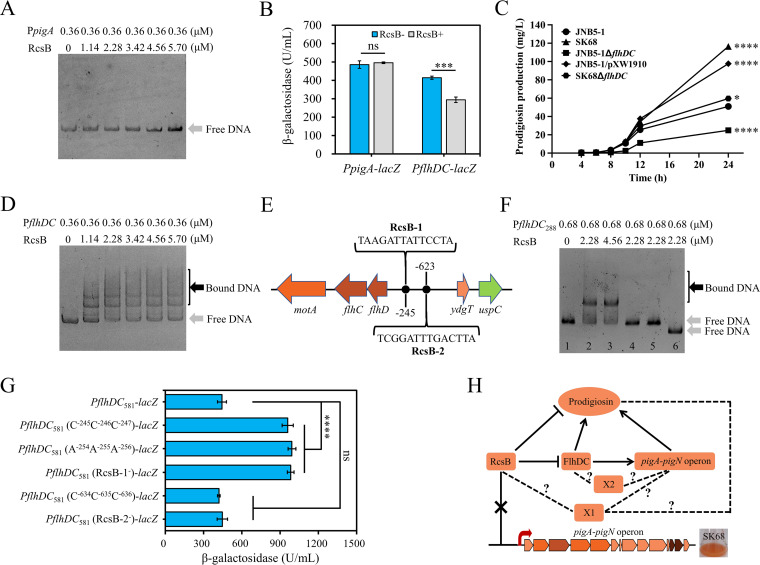
FIG 4.
RcsB regulates the prodigiosin synthesis genes indirectly. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for RcsB protein binding to the promoter region of the pig operon. (B) Overexpression of RcsB protein has no significant effect on the expression of the pig gene cluster, but it inhibits the expression of the flhDC genes in E. coli. The transcription fusions PpigA-lacZ and PflhDC-lacZ were used in the E. coli strains DH5α/pXW1908 (rcsB+) and DH5α/pUCP18 (rcsB negative). The plasmid pXW1908 carries the intact rcsB gene. The samples were collected at an OD600 of 4.0. (C) Prodigiosin production analysis of strains JNB5-1, SK68, JNB5-1ΔflhDC, JNB5-1/pXW1910, and SK68ΔflhDC. JNB5-1 is a wild-type S. marcescens strain, SK68 is an rcsB-disrupted mutant, JNB5-1ΔflhDC is an flhDC deletion mutant, JNB5-1/pXW1910 is an rcsB-overexpressing mutant, and SK68ΔflhDC is an rcsB flhDC double mutant. (D) EMSA for RcsB protein binding to the promoter region of the flhDC genes. (E) Putative RcsB binding sites in the promoter region of flhDC genes in S. marcescens. The positions of the binding sites are numbered relative to the translational start site of the flhD gene. (F) EMSA results revealed that RcsB could specifically bind to the binding site RcsB-1 in vitro. PflhDC288, a 288-bp DNA fragment from nucleotide positions −86 to −373 relative to the translational start site of flhD gene. Lane 1, PflhDC288 without protein RcsB. Lane 2, PflhDC288 with 2.28 μM RcsB. Lane 3, PflhDC288 with 4.56 μM RcsB. Lane 4, PflhDC288 carrying mutations in positions TAA with protein RcsB. Lane 5, PflhDC288 carrying mutations in positions TCC with protein RcsB. Lane 6, PflhDC288 with complete deletion of RcsB-1. (G) In vivo analysis of the S. marcescens flhDC RcsB binding site by mutagenesis. The transcription fusions PflhDC581-lacZ, PflhDC581 (C−245C−246C−247)-lacZ, PflhDC581 (A−254A−255A−256)-lacZ, PflhDC581 (RcsB-1−)-lacZ, PflhDC581 (C−634C−635C−636)-lacZ, and PflhDC581 (RcsB-2−)-lacZ were used in the S. marcescens strain JNB5-1. PflhDC581, DNA fragment containing the binding sites RcsB-1 and RcsB-2; PflhDC581 (C−245C−246C−247), PflhDC581 carrying mutations in positions TAA; and PflhDC581 (A−254A−255A−256), PflhDC581 carrying mutations in positions TCC; PflhDC581 (RcsB-1−), PflhDC581 with complete deletion of RcsB-1; PflhDC581 (C−634C−635C−636), PflhDC581 carrying mutations in positions TTA; and PflhDC581 (RcsB-2−), PflhDC581 with complete deletion of RcsB-2. (H) The regulatory network of RcsB controls prodigiosin synthesis in S. marcescens. The pigA to pigN operon includes genes pigABCDEFGHIJKLMN, a total of 14 genes. RcsB is an inhibitor for prodigiosin synthesis, and FlhDC is an activator for prodigiosin synthesis. X1 indicates an unknown prodigiosin synthesis regulator controlled by RcsB. X2 indicates an unknown regulator which may be regulated by FlhDC. Arrows indicate positive regulation, and T-shaped lines indicate negative regulation. Dotted lines indicate additional pathways that influence RcsB or FlhDC control of prodigiosin production. (B and C) Experiments were performed in biological triplicates. Error bars indicate the standard deviations. (B) Student's t test was used for statistical analysis. (C) One-way ANOVA was used to examine the mean differences between the data groups. ****, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05.