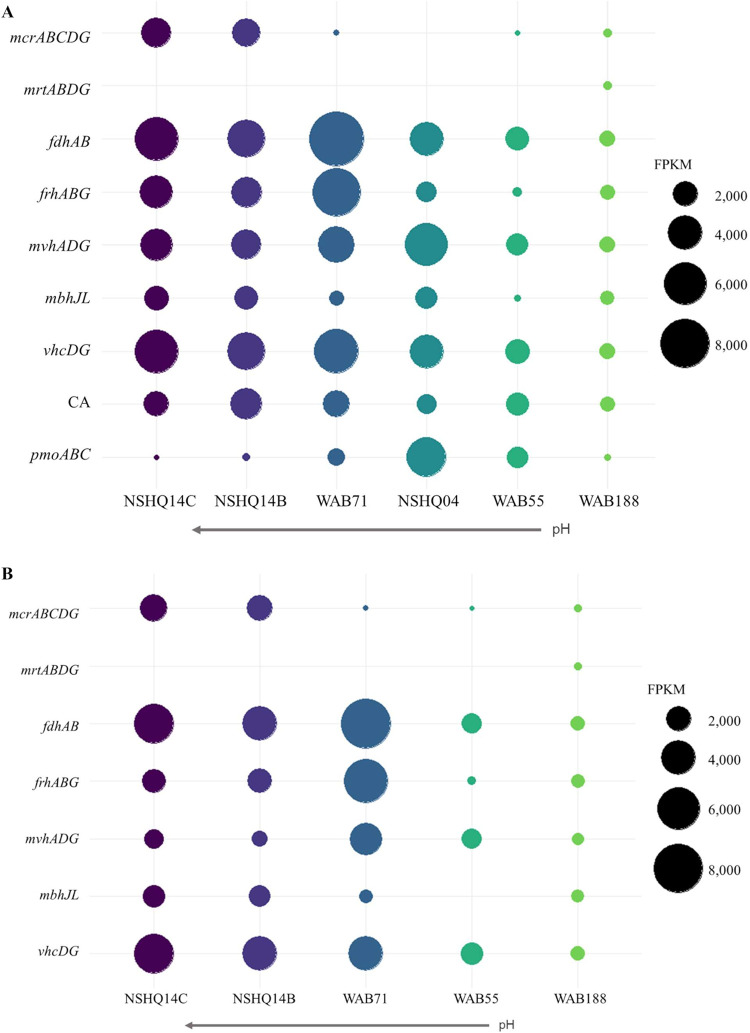
FIG 3.
(A) Fragments per kilobase of exon per million reads (FPKM) of key functional genes of interest for CH4 cycling metabolisms. The methyl-coenzyme M I (mcrABGCD), methyl-coenzyme M II (mrtABGD), formate dehydrogenase (fdhAB), carbonic anhydrase (CA), particulate methane monooxygenase (pmoABC), and methanogenic [NiFe]-hydrogenase (frh, mvh, mbh, and vhc) enzymes from assembled metagenomes are shown. Notably, FPKM values are comparable within each sample (shown by color) but not across samples. Wells are ordered by decreasing fluid pH. (B) FPKM of CH4 cycling genes that are homologous to proteins from Methanobacterium sp. (E value of < 1 × 10−6; >30% amino acid identity over >50% of the length).