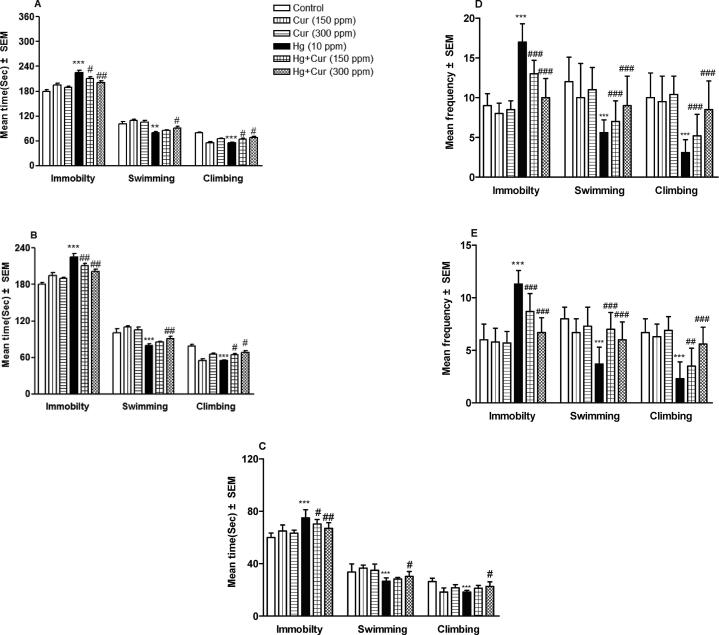
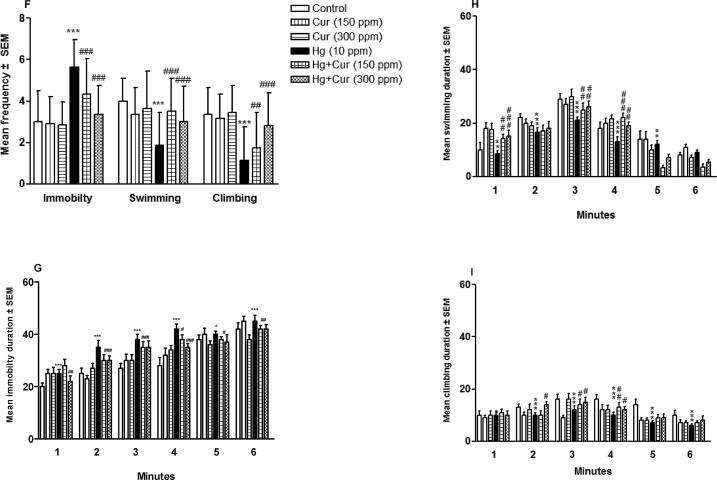
Fig. 2.
A–I. Perinatal exposure to mercury (Hg) and curcumin (Cur) on depression of mice offspring in (A, B and C) forced swimming test, showing immobility, swimming and climbing behavioral results after 6 min (A), 4 min (B) and 2 min (C) respectively; (D, E and F) shows frequency of immobility, swimming and climbing behavioral results after 6 min (D), 4 min (E) and 2 min (F) respectively; and (G, H and I) showing duration of immobility (G), swimming (H) and climbing (I) in total 6 min respectively.** and *** show statistically significant at P < 0.01 and P < 0.001 respectively compared to control, and #, ## and ### show statistically significant at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.001 respectively compared to Hg group by ANOVA and student's t-test.