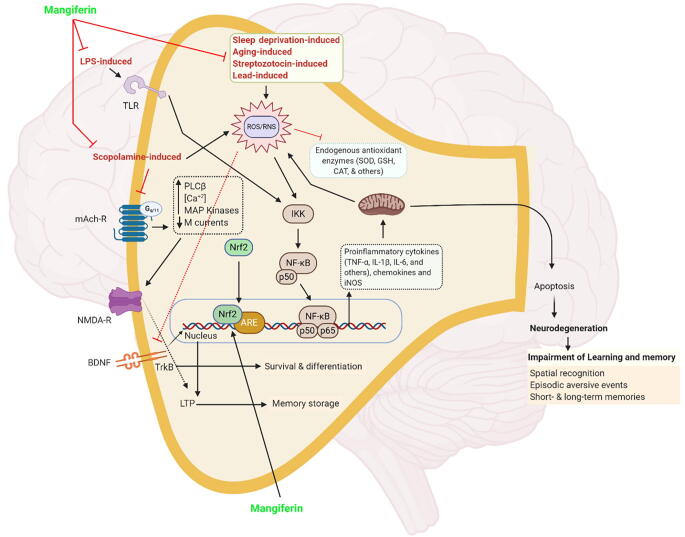
Fig. 4.
Molecular mechanism(s) of mangiferin. Induction of oxidative/nitrosative stress is a key factor in various memory impairment animal models, such as sleep deprivation-induced, ageing-induced, STZ-induced, and lead-induced models. Oxidative/nitrosative stress inhibits the endogenous antioxidant enzymes, and sequentially activates the proinflammatory cytokines secretion followed by dysregulation of mitochondrial function. The effects cumulatively lead to a programmed cell death (apoptosis) that causes neurodegeneration in hippocampus which facilitates memory impairment. In addition, LPS-induced model directly activates the pro-inflammatory cytokine signalling without activating ROS/RNS. Furthermore, scopolamine induces dysregulation of cholinergic activity and contribute to induction of oxidative stress. Mangiferin exerts its neuroprotective by inhibiting the oxidative/nitrosative stress and elevating the antioxidant mechanism. Finally, the endogenous anti-oxidative defense system induced by mangiferin occurs via activation of the nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) signalling pathway.Abbreviations, ARE, antioxidant response element, LTP, long-term potentiation., mAch-R, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, PLC, phospholipase C, TrkB, tropomyosin receptor kinase B, other abbreviations are available in the main text.