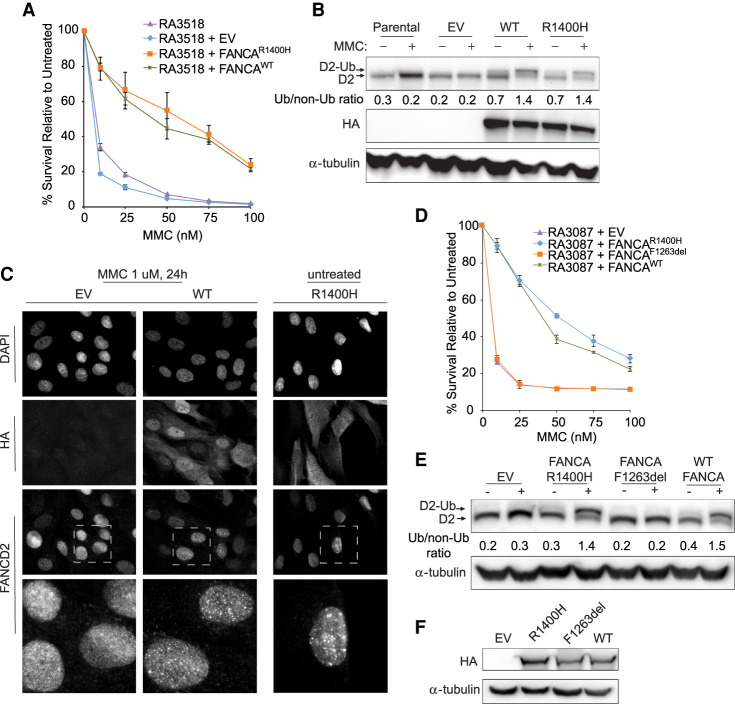
Figure 2.
Overexpression of FANCA R1400H rescues hypersensitivity to mitomycin C (MMC), FANCD2 ubiquitination, and localization of FANCD2 to sites of damage. (A) MMC cellular sensitivity assay of proband RA3518 fibroblasts with no vector expression (parental), expressing empty vector (EV), or overexpression of FANCA mutant (FANCAR1400H) or wild-type FANCA (FANCAWT). (B) Western blot assessing FANCD2 monoubiquitination and level of HA tagged FANCA expression in parental (no vector) and EV, FANCAR1400H, and FANCAWT expressing RA3518 fibroblasts. Cells were either untreated or cultured with 1 µM MMC for 24 h. (C) Immunofluorescence images with either anti-HA to detect overexpressed FANCA or anti-FANCD2 to detect FANCD2 localization to chromatin after treatment with 1 µM MMC for 24 h in RA3518 fibroblasts expressing EV, or overexpression of wild-type FANCA (FANCAWT) or FANCA mutant (FANCAR1400H). (D) MMC cellular sensitivity assay of FANCA-deficient RA3087 fibroblasts either expressing EV, a FANCA mutant (FANCAR1400H or FANCAF1263del), or wild-type FANCA (FANCAWT). (E) Western blot assessing FANCD2 monoubiquitination in FANCA deficient RA3087 fibroblasts overexpressing p.F1263del FANCA. Cells were either untreated or cultured with 1 µM MMC for 24 h. Relative ratio of monoubiquitinated to nonubiquitinated FANCD2 was measured for each variant. (F) Western blot assessing level of HA-tagged FANCA expression in RA3087 cells.