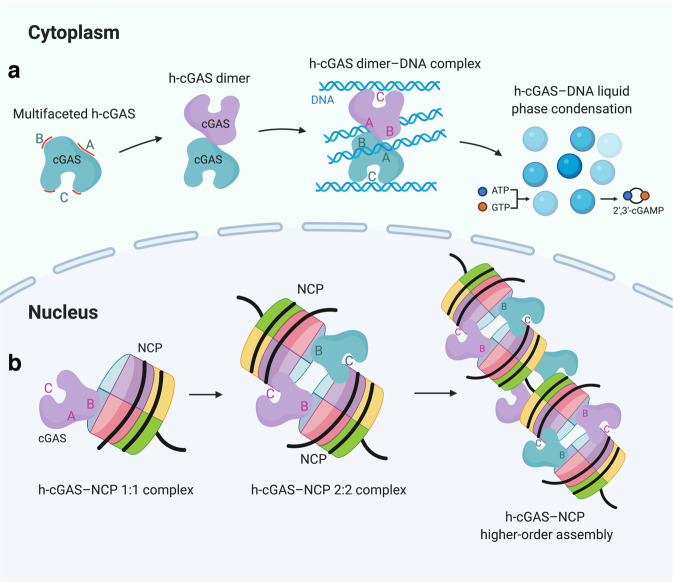
Fig. 1. Proposed models for inactivation of human cGAS by the nucleosome.
a In the cytoplasm, human cGAS (h-cGAS) proteins form dimers to sense cytosolic DNA with three DNA-binding sites (labeled A, B, and C), resulting in the formation of h-cGAS dimer–DNA clusters and h-cGAS–DNA liquid phase condensates, to activate the production of 2′,3′-cGAMP. b In the nucleus, the monomeric h-cGAS can bind NCPs with 1:1 and 2:2 stoichiometries, mediated by DNA-binding sites B and C. Furthermore, a proposed higher-order assembly of the h-cGAS–NCP complex could be indicative of a tighter tethering of h-cGAS by the nucleosomes due to a cooperative binding mechanism.