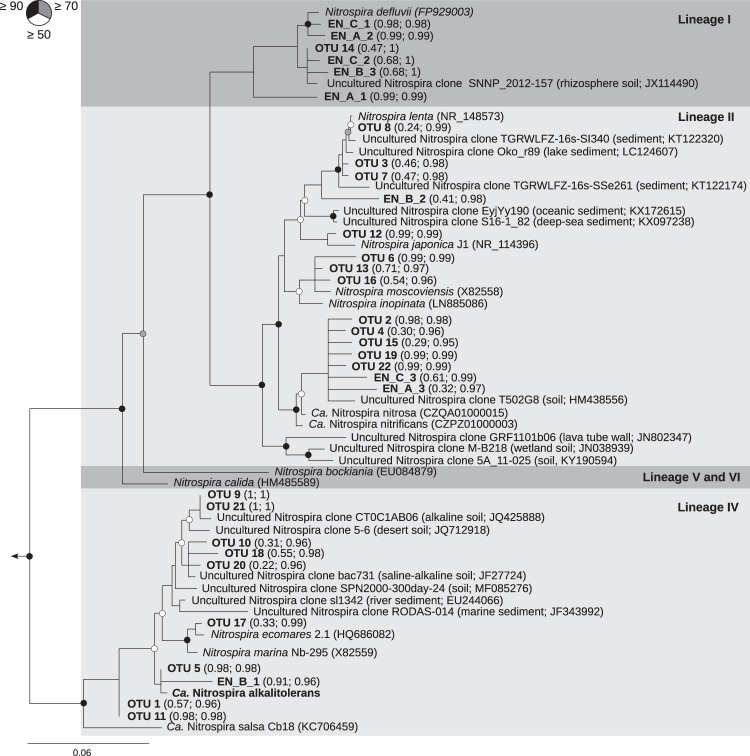
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic maximum likelihood analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequences of selected representatives from the genus Nitrospira and of the Nitrospira members detected in sediments from nine saline-alkaline lakes.
Sequences obtained in this study are printed in bold. “Ca. N. alkalitolerans” is the Nitrospira species cultured and further analyzed in this study. The tree was constructed using full length sequences and a 50% conservation filter resulting in 1310 valid alignment positions. Shorter sequences from this study, generated through amplicon and Sanger sequencing were added to the tree using the Evolutionary Placement Algorithm (EPA) without changing the overall tree topology. Numbers in brackets behind these sequences firstly denote the likelihood score of the exact placement and secondly the cumulative likelihood score of the placement within the cluster. Filled, gray, and open circles denote branches with ≥90%, ≥70% and ≥50% bootstrap support, respectively. Leptospirillum ferrooxidans (AJ237903), Ca. Magnetobacterium bavaricum (FP929063), Thermodesulfovibrio yellowstonii DSM 11347 (CP001147), and Ca. Methylomirabilis oxyfera (FP565575) were used as outgroup. The scale bar indicates 6% estimated sequence divergence.