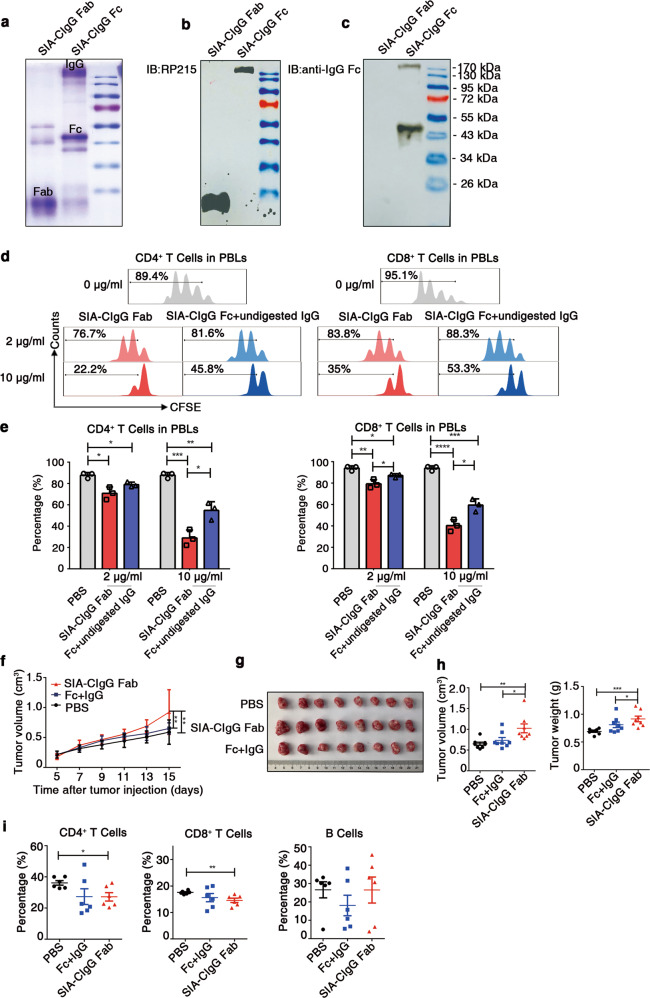
Fig. 5.
Fab fragments of SIA-CIgG containing the CH1 domain that are recognized by RP215 display a strong inhibitory effect on T-cell proliferation. a Coomassie light blue staining of SIA-CIgG Fab and SIA-CIgG Fc fragments digested by papain. The sialylation site was identified with RP215 (b) and a commercial anti-human-IgG Fc antibody (c) by western blotting. d SIA-CIgG Fab and SIA-CIgG Fc + undigested IgG fragments were digested by papain. Then, PBS, the SIA-CIgG Fab fragments or the SIA-CIgG Fc + undigested IgG fragments were added to peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) that were activated as described in Fig. 1f. The proliferation of CFSE-labeled CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was measured after 72 h. The doses of SIA-CIgG Fab fragments or SIA-CIgG Fc + undigested IgG fragments were 0 μg/ml, 2 μg/ml, and 10 μg/ml. e Proportions and statistical significance of proliferating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells among all PBLs treated with PBS, SIA-CIgG Fab fragments or SIA-CIgG Fc + undigested IgG fragments (Fc + undigested IgG) as described in (d) (n = 3 each group), as determined by flow cytometry. Small horizontal lines (e) indicate the mean (± s.d.). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001 (two-tailed Student’s t test for unpaired data). Tumor growth curves (f), tumor images (g), and tumor volume and weight (h) were determined on the 15th day after injection of EMT-6 cells into BALB/c mice (PBS, n = 8; SIA-CIgG Fab, 20 μg, n = 8; and SIA-CIgG Fc + undigested IgG, 20 μg, n = 8). i Proportions of lymphocytes in the tumors of mice treated with PBS (n = 8), SIA-CIgG Fab fragments (n = 8), or SIA-CIgG Fc + undigested IgG fragments (Fc + IgG) (n = 8). Each symbol represents an individual tumor sample; small horizontal lines indicate the mean ( ± s.e.m.). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test). Data are from one experiment that was representative of three (a–d) or two (f–i) independent experiments with similar results.