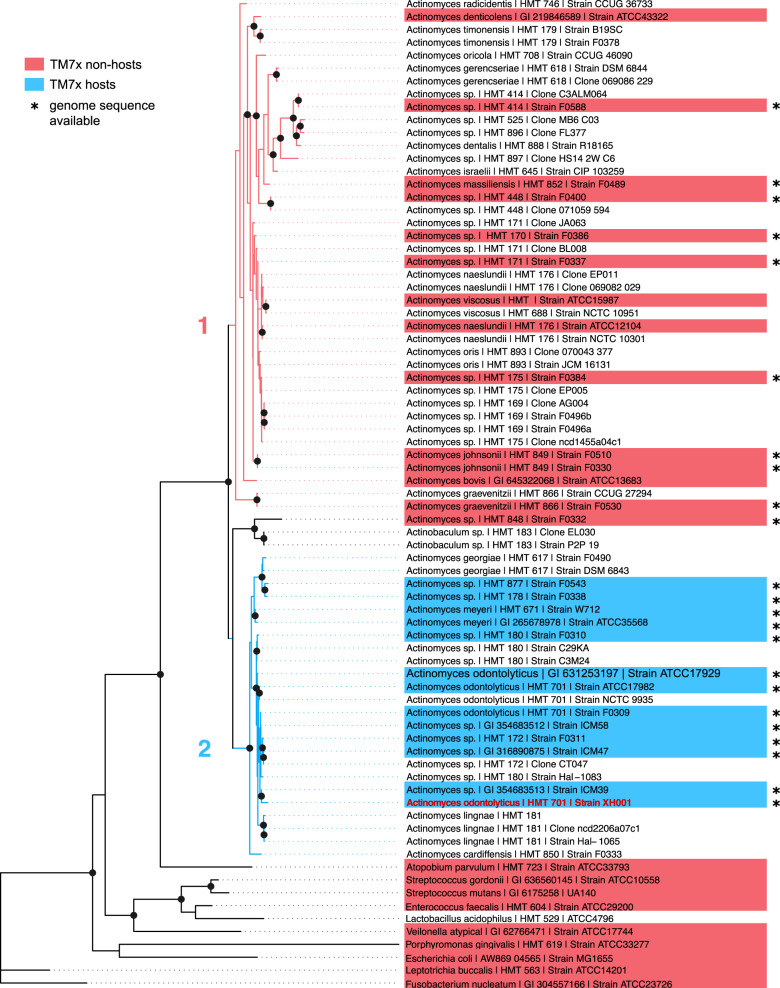
Fig. 1. TM7x host-range. Different Actinomyces and oral bacterial species (highlighted) were tested for TM7x re-infection.
A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was created using the 16S rRNA gene sequences of candidate hosts, which revealed two Actinomyces clades (1 and 2). XH001 (orange) is the host with which TM7x was originally isolated. Susceptible and resistant strains are shown in blue and red, respectively. Bacteria included for phylogenetic analysis but not tested for TM7x susceptibility are not highlighted. The 23 strains indicated by asterisks have sequenced genomes publicly available. The scale is 4 substitutions per site. Nodes with bootstrap support ≥70 are marked with a black dot.