Fig 4. piRNAs are produced from both TART-A and nxf2.
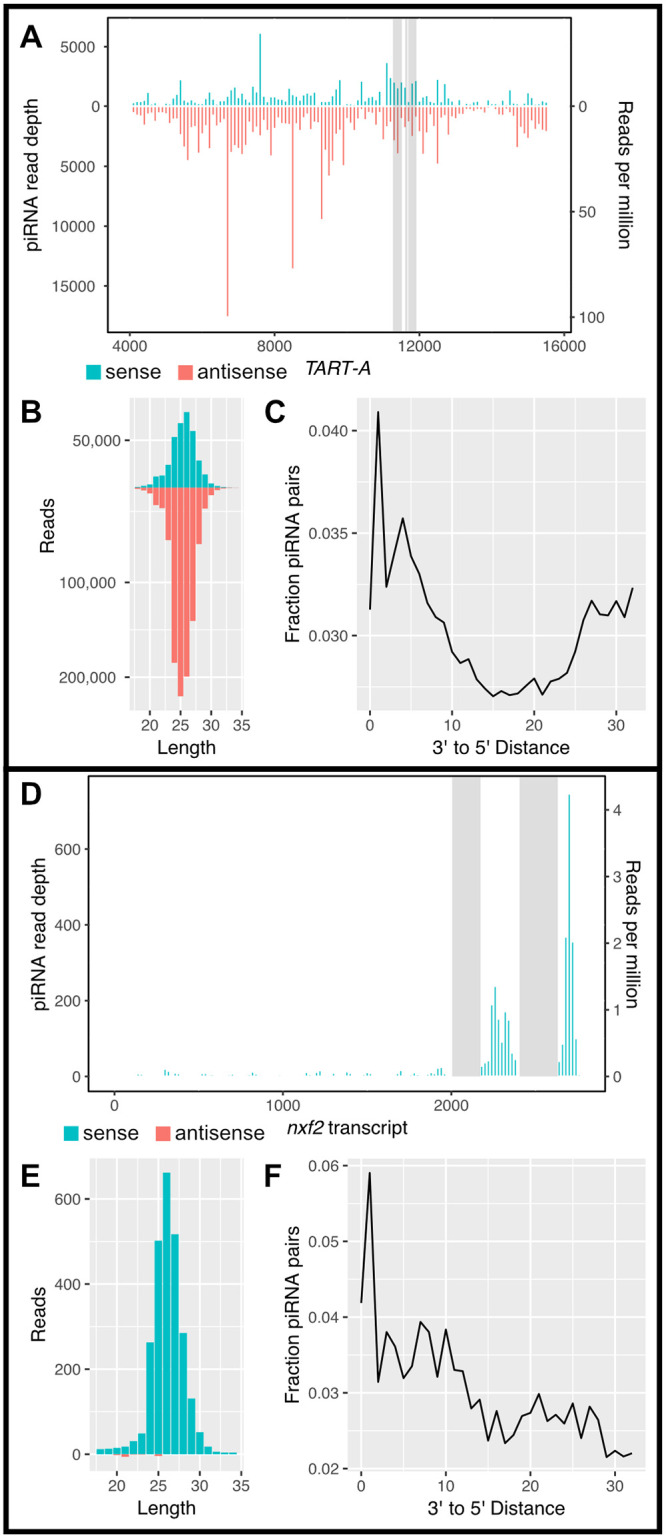
(A) We aligned previously published piRNA data from the D. melanogaster DGRP [85] to TART-A and examined read coverage across the element. We find abundant sense (blue bars) and antisense (red bars) piRNA production across most of the element, including the regions containing the nxf2-like sequence (gray boxes). Note that the 5′ UTR of TART-A is copied from the 3′ UTR during replication and is therefore identical in sequence. We masked the 5′ UTR (positions 1–4,000) for this analysis. (B) The length of aligned reads are consistent with that expected for piRNAs and the TART-A derived piRNAs are biased toward the minus strand. (C) TART-A piRNAs show an enrichment of alignments where the 5′ end of 1 piRNA is found directly after the 3′ end of the previous piRNA (i.e., distance of 1), consistent with piRNA phasing. (D) Unlike TART-A, nxf2 produces piRNAs primarily in the regions directly downstream from its TART-like sequence (gray boxes). The vast majority of these piRNAs are only from the sense strand of nxf2 (E) and also show the signature of phasing (F). Note that the TART-like sequence of nxf2 was masked for this analysis to avoid cross-mapping of TART-derived piRNAs to the nxf2 transcript. Underlying data can be found in S2 Data. piRNA, Piwi-interacting small RNA; TE, transposable element.
