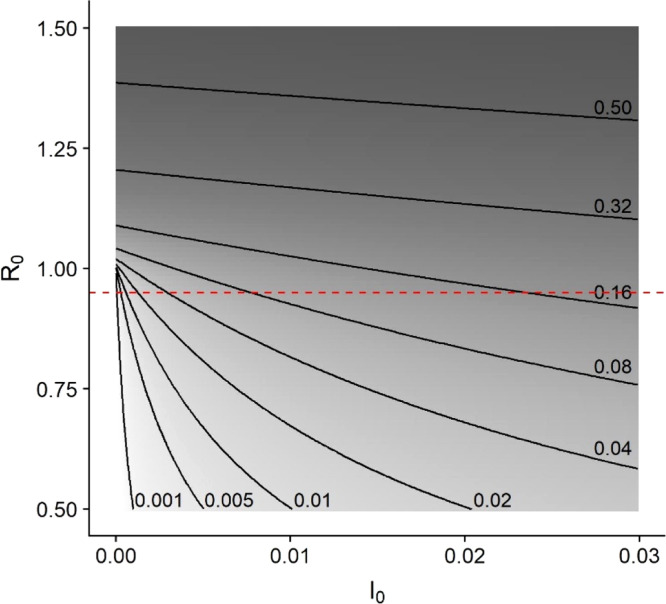
Fig. 3.
Epidemic size contours and shading show that when is close to 1, the epidemic is more strongly influenced by a reduction of than by a reduction of . For instance, if (dashed line), the epidemic could infect from less than 0.1% to greater than 16% of the population as ranges from just above 0% to 3% of the population. Epidemic size was calculated using the final size equation, , where . Shading indicates the cube root of epidemic size with lighter colors corresponding to smaller outbreaks.