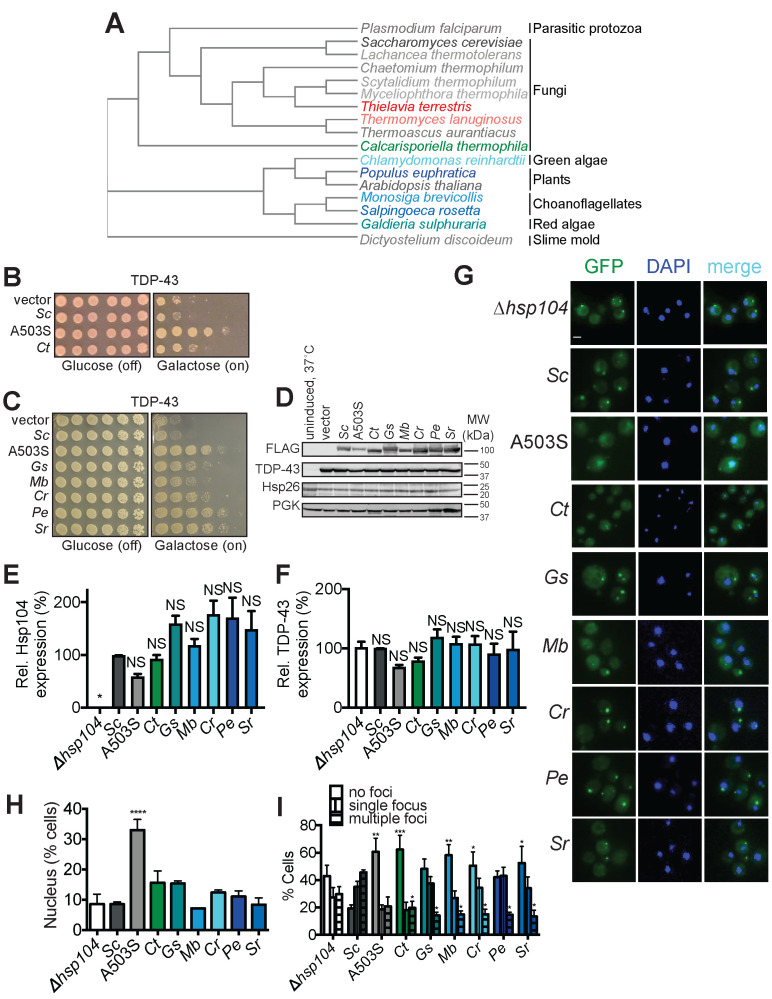
Figure 1. Diverse Hsp104 homologs suppress TDP-43 toxicity in yeast.
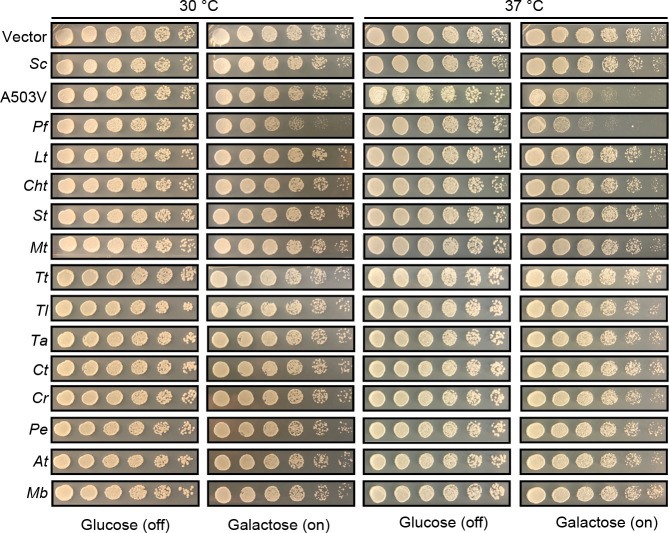
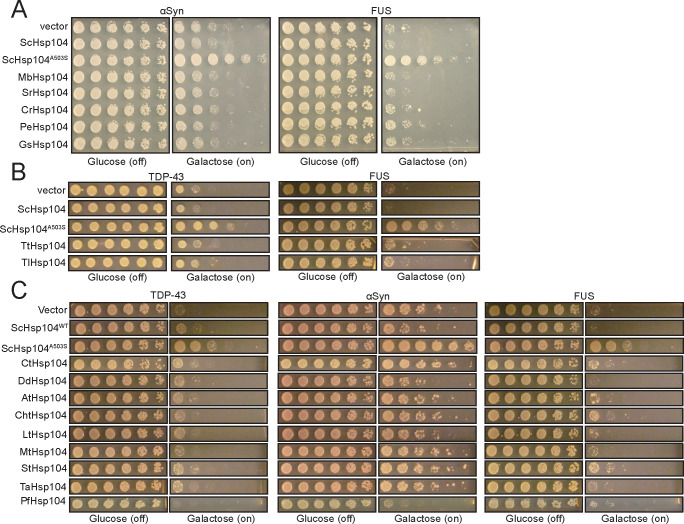
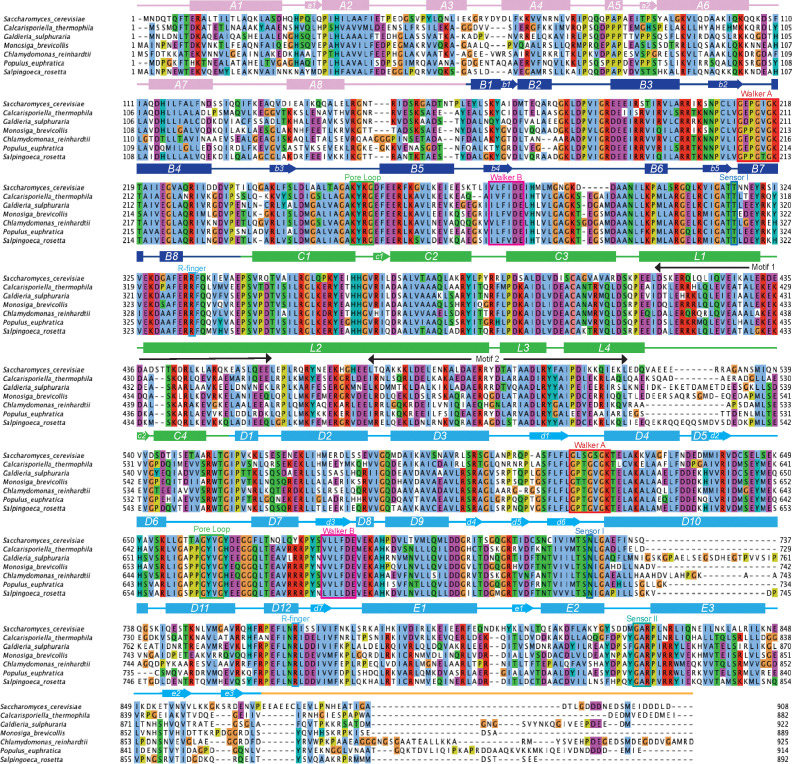
(A) Phylogenetic tree constructed using EMBL-EBI Simple Phylogeny tool from a multiple sequence alignment of the indicated Hsp104 homologs generated in Clustal Omega (see also Supplemental Information for alignments) showing evolutionary relationships between Hsp104 homologs studied in this paper. C. thermophila is in green, TDP-43-specific homologs are colored in shades of blue, αSyn-specific homologs are colored in red, and non-rescuing homologs are colored in shades of gray. (B) Δhsp104 yeast transformed with plasmids encoding galactose-inducible TDP-43 and the indicated galactose-inducible Hsp104 (either wild-type Hsp104 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the potentiated variant A503S, or the Hsp104 homolog from Calcarisporiella thermophila (Ct)) were serially diluted 5-fold and spotted onto glucose (expression off) or galactose (expression on). (C) Δhsp104 yeast transformed with plasmids encoding galactose-inducible TDP-43 and the indicated galactose-inducible Hsp104 (either wild-type Hsp104 from S. cerevisiae, the potentiated variant A503S, or homologs from Galdieria sulphuraria (Gs), Monosiga brevicollis (Mb), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr), Populus euphratica (Pe), and Salpingoeca rosetta (Sr)) were serially diluted 5-fold and spotted onto glucose (expression off) or galactose (expression on). (D) Western blots confirm consistent expression of FLAG-tagged Hsp104s and proteotoxic protein substrates in yeast, and that neither Hsp104 expression nor TDP-43 expression induces upregulation of the endogenous heat-shock protein Hsp26. The first lane are isogenic yeast that have not been grown in galactose to induce Hsp104 and TDP-43 expression but instead have been pretreated at 37°C for 30 min to upregulate endogenous heat-shock proteins. 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) is used as a loading control. Molecular weight markers are indicated (right). (E) Expression of the indicated Hsp104-FLAG relative to PGK was quantified for each strain. Values are means ± SEM (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was used to compare expression of ScHsp104-FLAG (Sc) to all other conditions. *p<0.05; NS, not significant. (F) TDP-43 expression relative to PGK was quantified for each strain. Values are means ± SEM (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was used to compare TDP-43 levels in the ∆hsp104 control to all other conditions. NS, not significant. (G) Representative images of yeast co-expressing TDP-43-GFPS11 (and separately GFPS1-10 to promote GFP reassembly) and the indicated Hsp104 homologs. Cells were stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei (blue). Scale bar, 2.5 µm. (H) Quantification of cells where TDP-43 displays nuclear localization. Values represent means ± SEM (n = 3 trials with >200 cells counted per trial). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was used to compare Δhsp104 to all other conditions. ****p<0.0001. (I) Quantification of cells with no, single, or multiple TDP-43 foci. Values represent means ± SEM (n = 3). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used to compare the proportion of cells with either no or multiple TDP-43 foci between strains expressing different Hsp104 homologs and a control strain expressing ScHsp104. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.