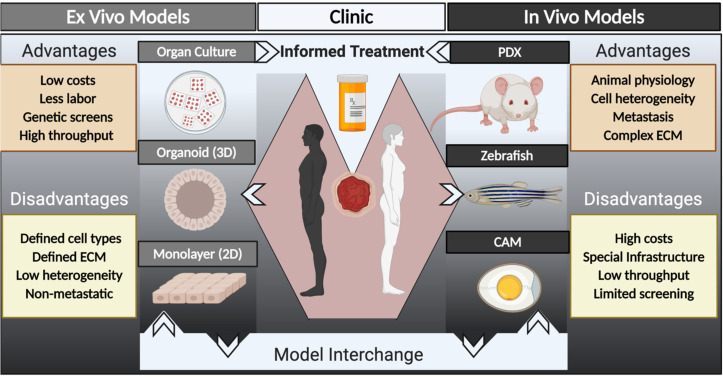
FIG. 1.
Schematic illustrating multiple platforms available for patient-derived models of cancer. Ex vivo and in vitro models (left side) include organ or tissue slice cultures, three-dimensional (3D) organoids, and two-dimensional (2D) monolayer cultures. In vivo models (right side) include patient-derived xenografts (PDX) in mouse, zebrafish, and chicken egg chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) hosts. Information from these model systems can be interchanged to increase our understanding of human cancer biology, to perform drug screening or testing, and, in some cases, for functional precision oncology to inform patient care.